Extractive-liquid sampling electron ionization-mass spectrometry (E-LEI-MS): a new powerful combination for direct analysis
- PMID: 37081134
- PMCID: PMC10119378
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-33647-5
Extractive-liquid sampling electron ionization-mass spectrometry (E-LEI-MS): a new powerful combination for direct analysis
Abstract
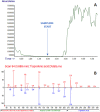
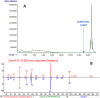
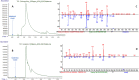
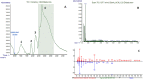
One of modern analytical chemistry main challenges is providing as fast as possible results in different application fields. In this view, real-time analysis techniques are experiencing ever-increasing success as they can provide data quickly, almost without sample preparation steps. Most of real-time approaches are based on direct mass spectrometry (DMS), a method of analyzing samples without the need for separation or pre-treatment steps. Instead, the sample is directly introduced into the mass spectrometer for analysis. In this context, ambient ionization mass spectrometry (AIMS) techniques are widely represented and successfully used. Extractive-liquid sampling electron ionization-mass spectrometry (E-LEI-MS) represents a different analytical strategy that allows coupling ambient sampling with electron ionization (EI), avoiding any sample preparation step and providing identification based on the comparison with the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) library spectra. E-LEI-MS consists of a dispositive for solvent release and sampling at ambient conditions coupled with an EI source of a single quadrupole mass spectrometer. A micromanipulator allows fine (x,y,z) positioning of a sampling tip. MS can operate in scan or SIM modes depending on the application goals and requirements. Several preliminary successful results were already obtained due to the highly informative EI mass spectra generation. The system was applied to the analysis of active ingredients in pharmaceutical tablets, pesticides on fruit peel, a drug of abuse (cocaine) determination in banknotes, and analysis of unknown components on painting surfaces. Both forensic and artwork applications allowed determining the spatial distribution of the analytes. Here we present a proof-of-concept of E-LEI-MS for targeted/non-targeted analysis and semi-quantitative detection.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Latest Developments in Direct and Non-Direct LC-MS Methods Based on Liquid Electron Ionization (LEI).Crit Rev Anal Chem. 2024 Jul 24:1-18. doi: 10.1080/10408347.2024.2381543. Online ahead of print. Crit Rev Anal Chem. 2024. PMID: 39046707 Review.
-
Flow injection of liquid samples to a mass spectrometer with ionization under vacuum conditions: a combined ion source for single-photon and electron impact ionization.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2013 Sep;405(22):6953-7. doi: 10.1007/s00216-013-7151-3. Epub 2013 Jun 30. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2013. PMID: 23812882
-
Liquid electron ionization-mass spectrometry as a novel strategy for integrating normal-phase liquid chromatography with low and high-resolution mass spectrometry.Analyst. 2024 Apr 29;149(9):2664-2670. doi: 10.1039/d3an02109b. Analyst. 2024. PMID: 38363103
-
Evaluation of a liquid electron ionization liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry interface.J Chromatogr A. 2019 Apr 26;1591:120-130. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2019.01.034. Epub 2019 Jan 11. J Chromatogr A. 2019. PMID: 30660440
-
NanoLC-EI-MS: Perspectives in Biochemical Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 21;24(14):11746. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411746. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511506 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sample Injection for Real-Time Analysis (SIRTA) Using GC-MS with Cold EI.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2024 Feb 7;35(2):378-385. doi: 10.1021/jasms.3c00412. Epub 2024 Jan 17. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2024. PMID: 38234102 Free PMC article.
-
Drug screening in pharmaceutical and forensic applications using extractive-liquid sampling electron ionization-mass spectrometry (E-LEI-MS).Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 20;15(1):30578. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-14772-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40836049 Free PMC article.
-
Coupling Miniaturized Stir Bar Sorptive Dispersive Microextraction to Needle-Based Electrospray Ionization Emitters for Mass Spectrometry: Determination of Tetrahydrocannabinol in Human Saliva as a Proof of Concept.Anal Chem. 2024 Jun 11;96(23):9629-9635. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.4c01297. Epub 2024 May 14. Anal Chem. 2024. PMID: 38743697 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Van Berkel GJ, Kertesz V. Continuous-flow liquid microjunction surface sampling probe connected on-line with high-performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry for spatially resolved analysis of small molecules and proteins. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2013;27:1329–1334. doi: 10.1002/rcm.6580. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

