Cell Cycle-Related FAM64A Could be Activated by TGF-β Signaling to Promote Glioma Progression
- PMID: 37081231
- PMCID: PMC11410130
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-023-01348-2
Cell Cycle-Related FAM64A Could be Activated by TGF-β Signaling to Promote Glioma Progression
Abstract
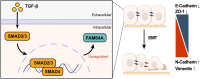
Gliomas are aggressive brain tumors characterized by uncontrolled cell proliferation. FAM64A, a cell cycle-related gene, has been found to promote cell proliferation in various tumors, including gliomas. However, the regulatory mechanism and clinical significance of FAM64A in gliomas remain unclear. In this study, we investigated FAM64A expression in gliomas with different grades and constructed FAM64A silenced cell lines to study its functions. Our results demonstrated that FAM64A was highly expressed in glioblastoma (P < 0.001) and associated with a poor prognosis (P < 0.001). Expression profiles at the single-cell resolution indicated FAM64A could play a role in a cell-cycle-dependent way to promote glioma cell proliferation. We further observed that FAM64A silencing in glioma cells resulted in disrupted proliferation and migration ability, and increased cell accumulation in the G2/M phase (P = 0.034). Additionally, TGF-β signaling upregulates FAM64A expression, and SMAD4 and FAM64A co-localize in high-grade glioma tissues. We found FAM64A knockdown inhibited TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in glioma. Our findings suggest that FAM64A could serve as a diagnostic and therapeutic target in gliomas.
Keywords: Cell cycle; EMT; FAM64A; Glioma; Single-cell RNA-seq; TGF-β.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Knockdown of FAM64A suppresses proliferation and migration of breast cancer cells.Breast Cancer. 2019 Nov;26(6):835-845. doi: 10.1007/s12282-019-00991-2. Epub 2019 Jul 1. Breast Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31264076
-
G-protein Coupled Receptor 34 Promotes Gliomagenesis by Inducing Proliferation and Malignant Phenotype via TGF-Beta/Smad Signaling Pathway.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2022 Jan-Dec;21:15330338221105733. doi: 10.1177/15330338221105733. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2022. PMID: 35770303 Free PMC article.
-
KIF4A promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition by activating the TGF-β/SMAD signaling pathway in glioma cells.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Jan;480(1):217-230. doi: 10.1007/s11010-024-04943-z. Epub 2024 Feb 27. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 38411896
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase subunit2 (CKS2) promotes malignant phenotypes and epithelial-mesenchymal transition-like process in glioma by activating TGFβ/SMAD signaling.Cancer Med. 2023 Mar;12(5):5889-5907. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5381. Epub 2022 Oct 25. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 36284444 Free PMC article.
-
Spalt-Like Transcription Factor 1 (SALL1) Gene Expression Inhibits Cell Proliferation and Cell Migration of Human Glioma Cells Through the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway.Med Sci Monit Basic Res. 2019 May 1;25:128-138. doi: 10.12659/MSMBR.915067. Med Sci Monit Basic Res. 2019. PMID: 31040265 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Knockout of the ING5 epigenetic regulator confirms roles in stem cell maintenance and tumor suppression in vivo.PLoS One. 2025 Jan 9;20(1):e0313255. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0313255. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39787145 Free PMC article.
-
FAM64A silencing inhibits the proliferation, migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in ovarian cancer cells via activating Hippo pathway.Discov Oncol. 2025 Jun 20;16(1):1160. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02710-0. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40537674 Free PMC article.
-
FAM64A regulates the malignant phenotype and tumor microenvironment of non-small cell lung cancer by activating the JAK/STAT3/PDL1 axis.J Mol Histol. 2025 Feb 24;56(2):95. doi: 10.1007/s10735-024-10339-6. J Mol Histol. 2025. PMID: 39992461
-
CDCA3 is a potential biomarker for glioma malignancy and targeted therapy.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 May 10;103(19):e38066. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038066. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38728485 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the prognostic significance of WDR77 in gliomas: a comprehensive analysis.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 21;15(1):13666. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-82867-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40258838 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Archangelo LF, Greif PA, Maucuer A, Manceau V, Koneru N, Bigarella CL, Niemann F, dos Santos MT, Kobarg J, Bohlander SK (1833) Saad ST (2013) The CATS (FAM64A) protein is a substrate of the kinase interacting stathmin (KIS). Biochim Biophys Acta 5:1269–1279. 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.02.004 - PubMed
-
- Bellail AC, Hunter SB, Brat DJ, Tan C, Van Meir EG (2004) Microregional extracellular matrix heterogeneity in brain modulates glioma cell invasion. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 36(6):1046–1069. 10.1016/j.biocel.2004.01.013 - PubMed
-
- Bronner SM, Merrick KA, Murray J, Salphati L, Moffat JG, Pang J, Sneeringer CJ, Dompe N, Cyr P, Purkey H, Boenig GL, Li J, Kolesnikov A, Larouche-Gauthier R, Lai KW, Shen X, Aubert-Nicol S, Chen YC, Cheong J, Crawford JJ, Hafner M, Haghshenas P, Jakalian A, Leclerc JP, Lim NK, O’Brien T, Plise EG, Shalan H, Sturino C, Wai J, Xiao Y, Yin J, Zhao L, Gould S, Olivero A, Heffron TP (2019) Design of a brain-penetrant CDK4/6 inhibitor for glioblastoma. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 29(16):2294–2301. 10.1016/j.bmcl.2019.06.021 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

