Magnetic resonance imaging at 9.4 T: the Maastricht journey
- PMID: 37081247
- PMCID: PMC10140139
- DOI: 10.1007/s10334-023-01080-4
Magnetic resonance imaging at 9.4 T: the Maastricht journey
Abstract
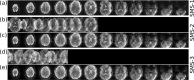
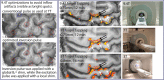
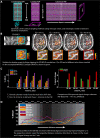
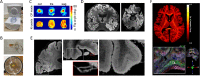
The 9.4 T scanner in Maastricht is a whole-body magnet with head gradients and parallel RF transmit capability. At the time of the design, it was conceptualized to be one of the best fMRI scanners in the world, but it has also been used for anatomical and diffusion imaging. 9.4 T offers increases in sensitivity and contrast, but the technical ultra-high field (UHF) challenges, such as field inhomogeneities and constraints set by RF power deposition, are exacerbated compared to 7 T. This article reviews some of the 9.4 T work done in Maastricht. Functional imaging experiments included blood oxygenation level-dependent (BOLD) and blood-volume weighted (VASO) fMRI using different readouts. BOLD benefits from shorter T2* at 9.4 T while VASO from longer T1. We show examples of both ex vivo and in vivo anatomical imaging. For many applications, pTx and optimized coils are essential to harness the full potential of 9.4 T. Our experience shows that, while considerable effort was required compared to our 7 T scanner, we could obtain high-quality anatomical and functional data, which illustrates the potential of MR acquisitions at even higher field strengths. The practical challenges of working with a relatively unique system are also discussed.
Keywords: 9.4 T; Ultra-high field; fMRI; pTx.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest in relation to the work described in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Le Ster C, Grant A, Van de Moortele PF, Monreal-Madrigal A, Adriany G, Vignaud A, Mauconduit F, Rabrait-Lerman C, Poser BA, Ugurbil K, Boulant N. Magnetic field strength dependent SNR gain at the center of a spherical phantom and up to 11.7T. Magn Reson Med. 2022;88(5):2131–2138. doi: 10.1002/mrm.29391. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 452-11-00/Nationaal Regieorgaan Onderwijsonderzoek
- 435-12-002/Nationaal Regieorgaan Onderwijsonderzoek
- 016-178-052/Nationaal Regieorgaan Onderwijsonderzoek
- 14637/Nationaal Regieorgaan Onderwijsonderzoek
- Multiconnect/H2020 European Research Council
- ERC - CoG 2020 - 101001270/H2020 European Research Council
- 720270 (HBP SGA1)/H2020 European Research Council
- ERC-2010-AdG 269853/H2020 European Research Council
- 785907 (HBP SGA2)/H2020 European Research Council
- 945539 (HBP SGA3)/H2020 European Research Council
- 101001270/H2020 European Research Council
- open grant AROMA No. 88587/H2020 Future and Emerging Technologies
- RF1MH116978-01/National Institute of Health (US)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

