The RNA m6A landscape of mouse oocytes and preimplantation embryos
- PMID: 37081317
- PMCID: PMC10337017
- DOI: 10.1038/s41594-023-00969-x
The RNA m6A landscape of mouse oocytes and preimplantation embryos
Abstract
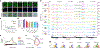
Despite the significance of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) in gene regulation, the requirement for large amounts of RNA has hindered m6A profiling in mammalian early embryos. Here we apply low-input methyl RNA immunoprecipitation and sequencing to map m6A in mouse oocytes and preimplantation embryos. We define the landscape of m6A during the maternal-to-zygotic transition, including stage-specifically expressed transcription factors essential for cell fate determination. Both the maternally inherited transcripts to be degraded post fertilization and the zygotically activated genes during zygotic genome activation are widely marked by m6A. In contrast to m6A-marked zygotic ally-activated genes, m6A-marked maternally inherited transcripts have a higher tendency to be targeted by microRNAs. Moreover, RNAs derived from retrotransposons, such as MTA that is maternally expressed and MERVL that is transcriptionally activated at the two-cell stage, are largely marked by m6A. Our results provide a foundation for future studies exploring the regulatory roles of m6A in mammalian early embryonic development.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





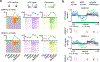





References
-
- Zaccara S, Ries RJ & Jaffrey SR Reading, writing and erasing mRNA methylation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 20, 608–624 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Klungland A, Dahl JA, Greggains G, Fedorcsak P. & Filipczyk A. Reversible RNA modifications in meiosis and pluripotency. Nat. Methods 14, 18–22 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Dominissini D. et al. Topology of the human and mouse m6A RNA methylomes revealed by m6A-seq. Nature 485, 201–206 (2012). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

