The Novel Biomarkers-Based HALP (Hemoglobin, Albumin, Lymphocyte and Platelet)-Prognostic Model for Acute and Subacute Patients with Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis: A Retrospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 37081612
- PMCID: PMC10627762
- DOI: 10.5551/jat.64043
The Novel Biomarkers-Based HALP (Hemoglobin, Albumin, Lymphocyte and Platelet)-Prognostic Model for Acute and Subacute Patients with Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
Aim: Increasing evidences suggest that HALP is an independent predictor of prognosis in patients with inflammation. However, the relationship between HALP and prognosis in patients with cerebral venous sinus thrombosis (CVST) has not been studied. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the prognosis values of HALP in acute or subacute CVST and explore the new prognostic model for CVST.
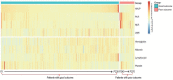
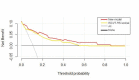
Methods: Consecutive patients who were diagnosed as having acute and subacute CVST were retrospectively investigated. We determined the patients' functional outcomes by modified Rankin Scale (mRS). Multivariate logistic regression analysis was used to assess the relationship between factors and poor functional outcomes. The area under the ROC curve (AUC) was estimated to evaluate the ability of markers and models in predicting clinical prognosis. The prognostic model was presented as nomogram. In addition, the decision curve analysis (DCA) was used to analyze the benefit of this model. Furthermore, survival curves were described by the Kaplan-Meier analysis.
Results: A total of 270 patients were included of which 31 had poor outcome. Multivariable logistic regression analysis demonstrated HALP (OR=0.978, 95%CI: 0.958-0.999, P=0.039) was a protective predictor of outcome. The AUC of HALP was 0.749 (95% CI: 0.633-0.865, P=0.044). DCA demonstrated that this model significantly improved risk prediction at threshold probabilities of CVST at 0 to 85% compared to ISCVT-RS scores. Patients with higher HALP (P=0.006) presented higher overall survival rates.
Conclusion: HALP may be a potential protective marker in acute and subacute CVST patients. The new prognostic model with HALP had potentially better value for acute and subacute CVST patients.
Keywords: Acute and subacute cerebral venous sinus thrombosis; Hemoglobin, Albumin, Lymphocyte, and Platelet (HALP); Prognostic model; Protective marker; Stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Prognostic value of systemic immune-inflammation index in acute/subacute patients with cerebral venous sinus thrombosis.Stroke Vasc Neurol. 2020 Dec;5(4):368-373. doi: 10.1136/svn-2020-000362. Epub 2020 Jun 24. Stroke Vasc Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32586971 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Thrombo-inflammatory Biomarkers in the Prognosis of Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis.Curr Neurovasc Res. 2021;18(2):237-243. doi: 10.2174/1567202618666210607151518. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2021. PMID: 34109909
-
[The clinical characteristics of neutrophil extracellular trap in patients with severe cerebral venous sinus thrombosis and its prognostic value in acute and subacute patients].Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024 May 1;62(5):443-451. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112139-20230926-00144. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38548615 Chinese.
-
Correlation analysis of hemoglobin, albumin, lymphocyte, platelet score and platelet to albumin ratio and prognosis in patients with lung adenosquamous carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2023 Sep 7;13:1166802. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1166802. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37746281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Key prognostic risk factors linked to poor functional outcomes in cerebral venous sinus thrombosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Neurol. 2025 Feb 6;25(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s12883-025-04059-x. BMC Neurol. 2025. PMID: 39915720 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The role of the hemoglobin-albumin-lymphocyte-platelet (HALP) score in deep neck infections and its relationship with clinical parameters.Turk J Med Sci. 2025 Mar 15;55(3):754-759. doi: 10.55730/1300-0144.6024. eCollection 2025. Turk J Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40686698 Free PMC article.
-
Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol-to-lymphocyte count ratio (LLR) is a promising novel predictor of postoperative new-onset deep vein thrombosis following open wedge high tibial osteotomy: a propensity score-matched analysis.Thromb J. 2024 Jul 16;22(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s12959-024-00635-2. Thromb J. 2024. PMID: 39014396 Free PMC article.
-
Hemoglobin albumin lymphocyte and platelet score and all-cause mortality in coronary heart disease: a retrospective cohort study of NHANES database.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Nov 13;10:1241217. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1241217. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 38028472 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of Two Potential Predictors of Thrombosis Risk in Polycythemia Vera: Hematocrit-to-Hemoglobin Ratio and HALP Score.Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2025 Jan-Dec;31:10760296251347630. doi: 10.1177/10760296251347630. Epub 2025 Jun 2. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2025. PMID: 40452364 Free PMC article.
-
The prognostic role of hemoglobin, albumin, lymphocyte, and platelets score in peritoneal dialysis.Int Urol Nephrol. 2025 Jul 23. doi: 10.1007/s11255-025-04679-9. Online ahead of print. Int Urol Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40699414
References
-
- Sader N, de Lotbinière-Bassett M, Tso MK, Hamilton M. Management of Venous Sinus Thrombosis. Neurosurg Clin N Am, 2018; 29: 585-594 - PubMed
-
- Coutinho JM, Zuurbier SM, Aramideh M, Stam J. The incidence of cerebral venous thrombosis: a cross-sectional study. Stroke, 2012; 43: 3375-3377 - PubMed
-
- Akboga YE, Bektas H, Anlar O. Usefulness of platelet to lymphocyte and neutrophil to lymphocyte ratios in predicting the presence of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis and in-hospital major adverse cerebral events. J Neurol Sci, 2017; 380: 226-229 - PubMed

