Origin of the Phosphoprotein Phosphatase (PPP) sequence family in Bacteria: Critical ancestral sequence changes, radiation patterns and substrate binding features
- PMID: 37082010
- PMCID: PMC10074919
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadva.2021.100005
Origin of the Phosphoprotein Phosphatase (PPP) sequence family in Bacteria: Critical ancestral sequence changes, radiation patterns and substrate binding features
Abstract
Background: Phosphoprotein phosphatases (PPP) belong to the PPP Sequence family, which in turn belongs to the broader metallophosphoesterase (MPE) superfamily. The relationship between the PPP Sequence family and other members of the MPE superfamily remains unresolved, in particular what transitions took place in an ancestral MPE to ultimately produce the phosphoprotein specific phosphatases (PPPs).
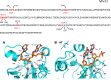
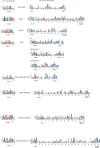
Methods: We use structural and sequence alignment data, phylogenetic tree analysis, sequence signature (Weblogo) analysis, in silico protein-peptide modeling data, and in silico mutagenesis to trace a likely route of evolution from MPEs to the PPP Sequence family. Hidden Markov Model (HMM) based iterative database search strategies were utilized to identify PPP Sequence Family members from numerous bacterial groups.
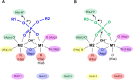
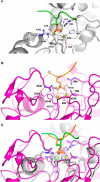
Results: Using Mre11 as proxy for an ancestral nuclease-like MPE we trace a possible evolutionary route that alters a single active site substrate binding His-residue to yield a new substrate binding accessory, the "2-Arg-Clamp". The 2-Arg-Clamp is not found in MPEs, but is present in all PPP Sequence family members, where the phosphomonesterase reaction predominates. Variation in position of the clamp arginines and a supplemental sequence loop likely provide substrate specificity for each PPP Sequence family group.
Conclusions: Loss of a key substrate binding His-in MPEs opened the path to bind novel substrates and evolution of the 2-Arg-Clamp, a sequence change seen in both bacterial and eukaryotic phosphoprotein phosphatases.General significance: We establish a likely evolutionary route from nuclease-like MPE to PPP Sequence family enzymes, that includes the phosphoprotein phosphatases.
Keywords: Bacterial origin; Metallophosphoesterase; Molecular dynamics simulation; Phosphomonoesterase; Phylogenetic analysis; Protein phosphatase.
© 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




References
-
- Cohen P. The regulation of protein function by multisite phosphorylation–a 25 year update. Trends Biochem Sci. 2000;25(12):596–601. - PubMed
-
- Sharma K., D'Souza R.C., Tyanova S., Schaab C., Wisniewski J.R., Cox J., Mann M. Ultradeep human phosphoproteome reveals a distinct regulatory nature of Tyr and Ser/Thr-based signaling. Cell Rep. 2014;8(5):1583–1594. - PubMed
-
- Manning G., Whyte D.B., Martinez R., Hunter T., Sudarsanam S. The protein kinase complement of the human genome. Science. 2002;298(5600):1912–1934. - PubMed
-
- Chen M.J., Dixon J.E., Manning G. Genomics and evolution of protein phosphatases. Sci Signal. 2017;10(474) - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

