Case report: Fulminant type 1 diabetes following paucisymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection during late pregnancy
- PMID: 37082120
- PMCID: PMC10112664
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1168927
Case report: Fulminant type 1 diabetes following paucisymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection during late pregnancy
Abstract
Background: Dysregulation of glucose metabolism has been linked to SARS-CoV-2 infection. In addition, the occurrence of new onset diabetes mellitus, including fulminant type 1 diabetes, has been reported after SARS-CoV-2 infection or vaccination.
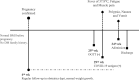
Methods and results: A young Chinese woman in her last trimester of pregnancy presented with an abrupt progression of hyperglycemia and ketoacidosis, but with a near-normal glycohemoglobin level following paucisymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. The low C peptide levels, both fasting and postprandial, reflected profound insulin deficiency in the setting of negative islet autoantibody testing, consistent with a diagnosis of fulminant type 1 diabetes. Ketoacidosis and hyperglycemia quickly improved following the introduction of insulin therapy, but not the β cell function. The patient received treatment with insulin pump therapy after being discharged, and the first follow-up revealed a well-controlled glucose profile.
Conclusions: New-onset FT1D can occur after SARS-CoV-2 infection. Our report raises awareness of this rare but serious situation, promoting early recognition and management of FT1D during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Keywords: case report; coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID- 19); fulminant type 1 diabetes; pregnancy; severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
Copyright © 2023 Zhou, Qu, Zhang, Hu and Shou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Case of new-onset fulminant type 1 diabetes mellitus accompanied by autoimmune thyroid disease after SARS-CoV-2 infection.Diabetol Int. 2024 May 30;15(3):621-626. doi: 10.1007/s13340-024-00729-2. eCollection 2024 Jul. Diabetol Int. 2024. PMID: 39101178 Free PMC article.
-
New-Onset Fulminant Type 1 Diabetes Following SARS-CoV-2 Protein Subunit Vaccine: A Case Report and Literature Review.J Korean Med Sci. 2023 Jun 19;38(24):e209. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e209. J Korean Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37337812 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New-onset fulminant type 1 diabetes after severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 vaccination: A case report.J Diabetes Investig. 2022 Jul;13(7):1286-1289. doi: 10.1111/jdi.13771. Epub 2022 Feb 25. J Diabetes Investig. 2022. PMID: 35167186 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 infection as possible downstream disease precipitator in autoantibody-positive insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: a case report.Ital J Pediatr. 2022 Feb 23;48(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s13052-022-01226-5. Ital J Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 35197086 Free PMC article.
-
Re-Enlightenment of Fulminant Type 1 Diabetes under the COVID-19 Pandemic.Biology (Basel). 2022 Nov 15;11(11):1662. doi: 10.3390/biology11111662. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36421377 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A case of new-onset Fulminant type 1 diabetes after secondary SARS-CoV-2 infection.Heliyon. 2024 May 4;10(9):e30750. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30750. eCollection 2024 May 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38756607 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial Extracellular Vesicles Enriched in microRNA-34a Predict New-Onset Diabetes in Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Patients: Novel Insights for Long COVID Metabolic Sequelae.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2024 Mar 15;389(1):34-39. doi: 10.1124/jpet.122.001253. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2024. PMID: 38336381 Free PMC article.
-
Pregnancy-associated fulminant type 1 diabetes: a case report and review of the literature.Diabetol Int. 2024 Mar 12;15(3):589-593. doi: 10.1007/s13340-024-00706-9. eCollection 2024 Jul. Diabetol Int. 2024. PMID: 39101176 Free PMC article.
-
Case of new-onset fulminant type 1 diabetes mellitus accompanied by autoimmune thyroid disease after SARS-CoV-2 infection.Diabetol Int. 2024 May 30;15(3):621-626. doi: 10.1007/s13340-024-00729-2. eCollection 2024 Jul. Diabetol Int. 2024. PMID: 39101178 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Imagawa A, Hanafusa T, Awata T, Ikegami H, Uchigata Y, Osawa H, et al. . Report of the committee of the Japan diabetes society on the research of fulminant and acute-onset type 1 diabetes mellitus: New diagnostic criteria of fulminant type 1 diabetes mellitus (2012). J Diabetes Investig (2012) 3(6):536–9. doi: 10.1111/jdi.12024 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous