Sphingolipids in thyroid eye disease
- PMID: 37082124
- PMCID: PMC10112667
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1170884
Sphingolipids in thyroid eye disease
Abstract
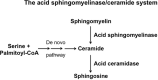
Graves' disease (GD) is caused by an autoimmune formation of autoantibodies and autoreactive T-cells against the thyroid stimulating hormone receptor (TSHR). The autoimmune reaction does not only lead to overstimulation of the thyroid gland, but very often also to an immune reaction against antigens within the orbital tissue leading to thyroid eye disease, which is characterized by activation of orbital fibroblasts, orbital generation of adipocytes and myofibroblasts and increased hyaluronan production in the orbit. Thyroid eye disease is the most common extra-thyroidal manifestation of the autoimmune Graves' disease. Several studies indicate an important role of sphingolipids, in particular the acid sphingomyelinase/ceramide system and sphingosine 1-phosphate in thyroid eye disease. Here, we discuss how the biophysical properties of sphingolipids contribute to cell signaling, in particular in the context of thyroid eye disease. We further review the role of the acid sphingomyelinase/ceramide system in autoimmune diseases and its function in T lymphocytes to provide some novel hypotheses for the pathogenesis of thyroid eye disease and potentially allowing the development of novel treatments.
Keywords: Graves’ disease; acid sphingomyelinase 2; ceramide; sphingolipids; thyroid eye disease (TED).
Copyright © 2023 Gulbins, Görtz, Gulbins and Eckstein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Linsitinib, an IGF-1R inhibitor, attenuates disease development and progression in a model of thyroid eye disease.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jun 26;14:1211473. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1211473. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37435490 Free PMC article.
-
Potential involvement of the bone marrow in experimental Graves' disease and thyroid eye disease.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Sep 22;14:1252727. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1252727. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37810891 Free PMC article.
-
[Pathogenesis of thyroid eye disease - does autoimmunity against the TSH receptor explain all cases?].Endokrynol Pol. 2011;62 Suppl 1:1-7. Endokrynol Pol. 2011. PMID: 22125104 Review. Polish.
-
Pathogenesis of thyroid eye disease--does autoimmunity against the TSH receptor explain all cases?Endokrynol Pol. 2010 Mar-Apr;61(2):222-7. Endokrynol Pol. 2010. PMID: 20464711 Review.
-
CD40 Enhances Sphingolipids in Orbital Fibroblasts: Potential Role of Sphingosine-1-Phosphate in Inflammatory T-Cell Migration in Graves' Orbitopathy.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018 Nov 1;59(13):5391-5397. doi: 10.1167/iovs.18-25466. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018. PMID: 30452592
Cited by
-
Linsitinib, an IGF-1R inhibitor, attenuates disease development and progression in a model of thyroid eye disease.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jun 26;14:1211473. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1211473. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37435490 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical