Comprehensive profiling of serotypes, antimicrobial resistance and virulence of Salmonella isolates from food animals in China, 2015-2021
- PMID: 37082181
- PMCID: PMC10110913
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1133241
Comprehensive profiling of serotypes, antimicrobial resistance and virulence of Salmonella isolates from food animals in China, 2015-2021
Abstract
Introduction: Salmonella is a ubiquitous foodborne pathogen and mainly transmitted to human farm-to-fork chain through contaminated foods of animal origin.
Methods: In this study, we investigated the serotypes, antimicrobial resistance and virulence of Salmonella from China.
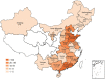
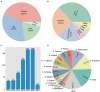
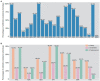
Results: A total of 617 Salmonella isolates were collected from 4 major food animal species across 23 provi nces in China from 2015-2021. Highest Salmonella prevalence were observed in Guangdong (44.4%) and Sandong (23.7%). Chickens (43.0%) was shown to be the major source of Salmonella contamination, followed by pigs (34.5%) and ducks (18.5%). The number of Salmonella increased significantly from 5.51% to 27.23% during 2015-2020. S. Derby (17.3%), S. Enteritidis (13.1%) and S. Typhimurium (11.4%) were the most common serotypes among 41 serotypes identifiedin this study. Antibiotic susceptibility testing showing that the majority of the Salmonella isolates were resistant to neomycin (99.7%), tetracycline (98.1%), ampicillin (97.4%), sulfadiazine/trimethoprim (97.1%), nalidixic acid (89.1%), doxycycline (83.1%), ceftria xone (70.3%), spectinomycin (67.7%), florfenicol (60.0%), cefotaxime (52.0%) and lomefloxacin (59.8%). The rates of resistance to multiple antibiotics in S. Derby and S.Typhimurium were higher than that in S. Enteritidis. However, the rate of resistance to fosfomycin were observed from higher to lower by S. Derby, S. Enteritidis, and S. Typhimurium. Biofilm formation ability analysis found that 88.49%of the Salmonella were able to produce biofilms, of which 236 Salmonella isolates were strong biofilm producer. Among the 26 types of antibiotics resistance genes (ARGs) were identified in this study, 4 ARGs (tetB,sul2,aadA2, and aph(3')-IIa) were highly prevalent. In addition, 5 β-lactam resistance genes (bla TEM, bla SHV, bla CMY-2, bla CTX-M, and bla OXA) and 7 quinolone resistance genes (oqxA, oqxB, qnrB, qnrC, qnrD, qnrS, and qeqA) were detected among these isolates. 12 out of 17 virulence genes selected in this study were commonly presented in the chromosomes of tested isolate, with a detection rate of over 80%, including misL, spiA, stn, pagC, iroN, fim, msgA, sopB, prgH, sitC, ttrC, spaN.
Discussion: This study provided a systematical updating on surveillance on prevalence of Salmonella from food animals in China, shedding the light on continued vigilance for Salmonella in food animals.
Keywords: Salmonella; biofilm formation; resistance genes; resistance phenotypes; virulence genes.
Copyright © 2023 Guo, Xiao, Wu, Li, Duan, Liu, Liu, Jin, Ren, Sun, Liu, Liao and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
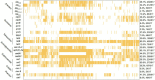
Similar articles
-
Occurrence of extended-spectrum β-lactamases among isolates of Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica from food-producing animals and food products, in Portugal.Int J Food Microbiol. 2013 Oct 15;167(2):221-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2013.08.009. Epub 2013 Aug 18. Int J Food Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 24135677
-
Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of retail-meat-borne Salmonella in southern China during the years 2009-2016: The diversity of contamination and the resistance evolution of multidrug-resistant isolates.Int J Food Microbiol. 2020 Nov 16;333:108790. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2020.108790. Epub 2020 Jul 14. Int J Food Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32693316
-
Antimicrobial susceptibility and virulence characteristics of Salmonella enterica Typhimurium isolates from healthy and diseased pigs in Korea.J Food Prot. 2014 Sep;77(9):1481-6. doi: 10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-14-084. J Food Prot. 2014. PMID: 25198838
-
Characteristics of Nontyphoid Salmonella Isolated from Human, Environmental, Animal, and Food Samples in Burkina Faso: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Jun 13;13(6):556. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13060556. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38927222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Systematic review on Prevalence, Serotypes and Antibiotic resistance of Salmonella in Ethiopia, 2010-2022.Infect Drug Resist. 2023 Oct 13;16:6703-6715. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S424345. eCollection 2023. Infect Drug Resist. 2023. PMID: 37854471 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Serovar and sequence type distribution and phenotypic and genotypic antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella originating from pet animals in Chongqing, China.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Jul 2;12(7):e0354223. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03542-23. Epub 2024 May 17. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38757951 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Salmonella enteritidis Infection and Mechanical Stress on Antimicrobial Peptide Expression in Hermetia illucens.Insects. 2025 Jul 4;16(7):692. doi: 10.3390/insects16070692. Insects. 2025. PMID: 40725322 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Resistance Genes and Clonal Relationships of Duck-Derived Salmonella in Shandong Province, China in 2023.Microorganisms. 2024 Dec 18;12(12):2619. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12122619. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39770821 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-genome sequencing-based characterization of Salmonella enterica Serovar Enteritidis and Kentucky isolated from laying hens in northwest of Iran, 2022-2023.Gut Pathog. 2025 Jan 16;17(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s13099-025-00679-3. Gut Pathog. 2025. PMID: 39819347 Free PMC article.
-
Genome analysis of colistin-resistant Salmonella isolates from human sources in Guizhou of southwestern China, 2019-2023.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jan 29;16:1498995. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1498995. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39944652 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akinyemi K. O., Iwalokun B. A., Foli F., Oshodi K., Coker A. O. (2011). Prevalence of multiple drug resistance and screening of enterotoxin (stn) gene in Salmonella enterica serovars from water sources in Lagos, Nigeria. Public Health 125, 65–71. doi: 10.1016/j.puhe.2010.11.010, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ammar A. M., Attia A. M. E., El-Aziz N. K. A., El-Hamid M. I. A., El-Demerdash A. S. (2016a). Class 1 integron and associated gene cassettes mediating multiple-drug resistance in some food borne pathogens. Int. Food Res. J. 23, 332–339. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00601-11 - DOI
-
- Ammendola S., Ajello M., Pasquali P., Kroll J. S., Langford P. R., Rotilio G., et al. . (2005). Differential contribution of sodC1 and sodC2 to intracellular survival and pathogenicity of Salmonella enterica serovar Choleraesuis. Microbes Infect. 7, 698–707. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2005.01.005, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

