Efficiency of Hesperidin against Liver Fibrosis Induced by Bile Duct Ligation in Rats
- PMID: 37082190
- PMCID: PMC10113046
- DOI: 10.1155/2023/5444301
Efficiency of Hesperidin against Liver Fibrosis Induced by Bile Duct Ligation in Rats
Abstract
Introduction: Bile duct ligation (BDL) and subsequent cholestasis are associated with oxidative stress and liver injury and fibrosis. Hesperidin (3,5,7-trihydroxyflavanone 7-rhamnoglucoside) is a flavanone glycoside abundant in citrus fruits. It has positive effects on diabetic retinopathy, reduced platelet aggregation, and blood flow alterations and has the potential to reduce liver injury in oxidative stress. The aim of this study was to evaluate the hepatoprotective effects of hesperidin on BDL-induced liver injury in rats.
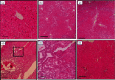
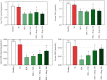
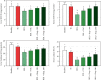
Methods: A total of 48 adult male Wistar rats were equally allocated to six eight-rat groups, namely, a healthy group, a sham group, a BDL+Vehicle group (BDL plus treatment with distilled water), a BDL+VitC group (BDL plus treatment with vitamin C 4.25 μg/kg), a BDL+Hesp100 group (BDL plus treatment with hesperidin 100 mg/kg/day), and a BDL+Hesp200 group (BDL plus treatment with hesperidin 200 mg/kg/day). Treatments were orally provided for 21 consecutive days. Finally, rats were sacrificed through heart blood sampling. Blood samples were centrifuged, and liver function, oxidative stress, and antioxidant parameters were assessed. Liver tissue was also assessed for oxidative stress, antioxidant, and histological parameters. The expression of inflammatory genes, namely, TGFβ1, iNOS, Caspase-3, and α-SMA, was measured through polymerase chain reaction. Findings. Hesperidin supplementation was associated with significant decrease in the levels of liver enzymes, bilirubin, nitric oxide, malondialdehyde, protein carbonyl, and inflammatory gene expression; significant increase in the levels of total antioxidant capacity, glutathione, and superoxide dismutase and catalase enzyme activity; and significant improvement in the histological morphology and structure of the liver parenchyma.
Conclusion: Hesperidin has significant positive effects on liver morphology and structure, inflammation, fibrosis, and oxidative stress in rats with BDL-induced cholestatic liver injury.
Copyright © 2023 Zahra Nasehi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Empagliflozin Exhibits Hepatoprotective Effects Against Bile Duct Ligation-induced Liver Injury in Rats: A Combined Molecular Docking Approach to In Vivo Studies.Curr Pharm Des. 2022;28(40):3313-3323. doi: 10.2174/1381612829666221027112239. Curr Pharm Des. 2022. PMID: 36305136
-
Hepatoprotective effect of astaxanthin against cholestasis liver fibrosis induced by bile duct ligation in adult Wistar rats.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2024 Aug;38(8):e23788. doi: 10.1002/jbt.23788. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39087918
-
The effects of hyperbaric oxygen application against cholestatic oxidative stress and hepatic damage after bile duct ligation in rats.J Surg Res. 2013 Jul;183(1):146-55. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2012.12.036. Epub 2013 Jan 9. J Surg Res. 2013. PMID: 23462455
-
Effects of hesperidin on anti-inflammatory and antioxidant response in healthy people: a meta-analysis and meta-regression.Int J Environ Health Res. 2023 Dec;33(12):1390-1405. doi: 10.1080/09603123.2022.2093841. Epub 2022 Jun 28. Int J Environ Health Res. 2023. PMID: 35762134 Review.
-
A comprehensive review on the impact of hesperidin and its aglycone hesperetin on metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and other liver disorders.Nutr Res Rev. 2024 Nov 26:1-13. doi: 10.1017/S0954422424000350. Online ahead of print. Nutr Res Rev. 2024. PMID: 39588563 Review.
Cited by
-
Long-term effects of warm water immersion on kidney tissue damage in diabetic rats.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2024;27(9):1162-1171. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2024.74307.16141. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39055872 Free PMC article.
-
Flavonoids in natural products for the therapy of liver diseases: progress and future opportunities.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Oct 24;15:1485065. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1485065. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39512816 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanism of the Effect of Compound Anoectochilus roxburghii (Wall.) Lindl. Oral Liquid in Treating Alcoholic Rat Liver Injury by Metabolomics.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023 Nov 15;17:3409-3428. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S427837. eCollection 2023. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023. PMID: 38024538 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Potential of Hesperidin in Preventing Hypertrophic Scars: Insights from a Rabbit Ear Model.Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023 Oct 19;16:2957-2963. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S428587. eCollection 2023. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 37876381 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced Insulin Resistance and Oxidative Stress in a Mouse Model of Metabolic Syndrome following Twelve Weeks of Citrus Bioflavonoid Hesperidin Supplementation: A Dose-Response Study.Biomolecules. 2024 May 29;14(6):637. doi: 10.3390/biom14060637. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38927040 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

