Antennal transcriptomic analysis of carboxylesterases and glutathione S-transferases associated with odorant degradation in the tea gray geometrid, Ectropis grisescens (Lepidoptera, Geometridae)
- PMID: 37082242
- PMCID: PMC10110894
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1183610
Antennal transcriptomic analysis of carboxylesterases and glutathione S-transferases associated with odorant degradation in the tea gray geometrid, Ectropis grisescens (Lepidoptera, Geometridae)
Abstract
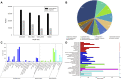
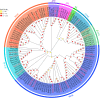
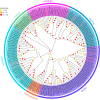
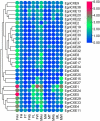
Introduction: Carboxylesterases (CXEs) and glutathione S-transferases (GSTs) can terminate olfactory signals during chemosensation by rapid degradation of odorants in the vicinity of receptors. The tea grey geometrid, Ectropis grisescens (Lepidoptera, Geometridae), one of the most devastating insect herbivores of tea plants in China, relies heavily on plant volatiles to locate the host plants as well as the oviposition sites. However, CXEs and GSTs involved in signal termination and odorant clearance in E. grisescens remains unknown. Methods: In this study, identification and spatial expression profiles of CXEs and GSTs in this major tea pest were investigated by transcriptomics and qRT-PCR, respectively. Results: As a result, we identified 28 CXEs and 16 GSTs from female and male antennal transcriptomes. Phylogenetic analyses clustered these candidates into several clades, among which antennal CXEs, mitochondrial and cytosolic CXEs, and delta group GSTs contained genes commonly associated with odorants degradation. Spatial expression profiles showed that most CXEs (26) were expressed in antennae. In comparison, putative GSTs exhibited a diverse expression pattern across different tissues, with one GST expressed specifically in the male antennae. Disscussion: These combined results suggest that 12 CXEs (EgriCXE1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 18, 20-22, 24, 26, and 29) and 5 GSTs (EgriGST1 and EgriGST delta group) provide a major source of candidate genes for odorants degradation in E. grisescens.
Keywords: Ectropis grisescens; antennal transcriptome; carboxylesterases; glutathione S-transferases; odorant-degrading enzyme.
Copyright © 2023 Zhang, Chen, Zhao, Guo, Hong, Zhi, Zhang, Zhou, Zhang, Zhou and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The reviewer WX declared a shared parent affiliation with the authors YZ and XL to the handling editor at the time of review.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Molecular Characterization and Functional Analysis of Odorant-Binding Proteins in Ectropis grisescens.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 10;26(10):4568. doi: 10.3390/ijms26104568. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40429713 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Expression Patterns of Putative Diversified Carboxylesterases in the Tea Geometrid Ectropis obliqua Prout.Front Physiol. 2017 Dec 18;8:1085. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.01085. eCollection 2017. Front Physiol. 2017. PMID: 29326608 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative expression profiles of carboxylesterase orthologous CXE14 in two closely related tea geometrid species, Ectropis obliqua Prout and Ectropis grisescens Warren.Front Physiol. 2023 May 24;14:1194997. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1194997. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37293262 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Candidate Carboxylesterases Associated With Odorant Degradation in Holotrichia parallela Antennae Based on Transcriptome Analysis.Front Physiol. 2021 Sep 10;12:674023. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.674023. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34566671 Free PMC article.
-
An Overview of Antennal Esterases in Lepidoptera.Front Physiol. 2021 Mar 31;12:643281. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.643281. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33868009 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Characterization and Functional Analysis of Odorant-Binding Proteins in Ectropis grisescens.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 10;26(10):4568. doi: 10.3390/ijms26104568. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40429713 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cano-Ramirez C., Lopez M. F., Cesar-Ayala A. K., Pineda-Martinez V., Sullivan B. T., Zúñiga G. (2013). Isolation and expression of cytochrome P450 genes in the antennae and gut of pine beetle Dendroctonus rhizophagus (Curculionidae: Scolytinae) following exposure to host monoterpenes. Gene 520 (1), 47–63. 10.1016/j.gene.2012.11.059 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

