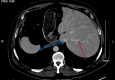
Ceftriaxone-Associated Severe Acute Hepatitis
- PMID: 37082506
- PMCID: PMC10110998
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.36341
Ceftriaxone-Associated Severe Acute Hepatitis
Abstract
Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a common entity. Ceftriaxone is a well-tolerated parenteral antibiotic widely used for various bacterial infections. We report a patient who developed severe acute hepatitis following a single dose of 2 g ceftriaxone within one day. Apart from a fever of 101.9 F, no other insult was noted to explain his severe hepatocellular injury around the time of presentation. On stopping further ceftriaxone, his symptoms resolved, and liver enzymes normalized within a week. His Roussel Uclaf Causality Assessment Method (RUCAM) score was 6 which suggested DILI be a probable cause of his acute hepatitis. Further surveillance at a larger scale is needed to support evidence for this rare side effect.
Keywords: ceftriaxone adverse effects; drug-induced liver injury (dili); elevated liver-associated enzymes; hepatitis; transaminitis.
Copyright © 2023, Asif et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Clinical evaluation of ceftriaxone. File TM Jr, Tan JS, Salstrom SJ. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6090021/ Clin Ther. 1984;6:653–661. - PubMed
-
- LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. [ Mar; 2023 ]. 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK548258/ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK548258/ - PubMed
-
- Drug-induced liver disease. Zimmerman HJ: Clin Liver Dis. 2000;4:73–96. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources