Synthesis of 1,3-Dioxan-2-ones by Photo-Aerobic Selenium-π-Acid Multicatalysis
- PMID: 37082528
- PMCID: PMC10108053
- DOI: 10.1002/ejoc.202201180
Synthesis of 1,3-Dioxan-2-ones by Photo-Aerobic Selenium-π-Acid Multicatalysis
Abstract
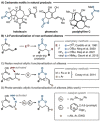
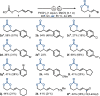
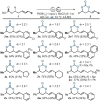
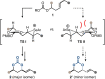
An expedient method for the synthesis of cyclic carbonates from homoallylic carbonic acid esters by means of photo-aerobic selenium-π-acid multicatalysis is reported. Until now, conceptually related methods commonly relied either on the stoichiometric addition of electrophiles onto the substrate's alkene moiety or the presence of pre-installed leaving groups in allylic position of said alkene to - in part, catalytically - initiate an intramolecular attack by an adjacent carbonic acid ester group. In sharp contrast, the current study shows that the C-C double bond of homoallylic carbonic acid esters can be directly activated by the catalytic interplay of a pyrylium dye and a diselane using ambient air as the sole oxidant and visible light as an energy source.
Keywords: 1,3-dioxan-2-ones; alkenes; allylic oxidation; photoredox catalysis; selenium-π-acid catalysis.
© 2022 The Authors. European Journal of Organic Chemistry published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- None
-
- Coates G. W., Moore D. R., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 6618–6639; - PubMed
- Angew. Chem. 2004, 116, 6784–6806;
-
- Darensbourg D. J., Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2388–2410; - PubMed
-
- Lu X.-B., Darensbourg D. J., Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 1462–1484; - PubMed
-
- Tempelaar S., Mespouille L., Coulembier O., Dubois P., Dove A. P., Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 1312–1336. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
