Promotion of liver fibrosis by Y-box binding protein 1 via the attenuation of transforming growth factor-beta 3 transcription
- PMID: 37082693
- PMCID: PMC10113103
- DOI: 10.21037/atm-23-835
Promotion of liver fibrosis by Y-box binding protein 1 via the attenuation of transforming growth factor-beta 3 transcription
Abstract
Background: Spurred by the seriousness of liver fibrosis, we evaluated the correlation between Y-box binding protein 1 (YB-1) and transforming growth factor-beta 3 (TGF-β3) expression levels in the signaling pathways of the disease.
Methods: Based on a mouse model of carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis, YB-1 overexpression lentivirus was used to explore the effect of YB-1 on liver fibrosis in vivo. In addition, a hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation model in the HSC line LX-2 was developed using TGF-β1. Western blot assays were used to investigate the effects of YB-1 overexpression and knockdown on liver fibrosis. Finally, chromatin immunoprecipitation and luciferase reporter assays were used to elucidate the relationship between YB-1 and its downstream signaling pathways.
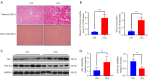
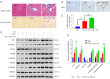
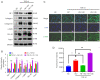
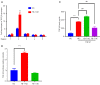
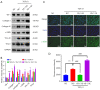
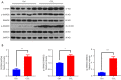
Results: YB-1 was overexpressed in fibrotic liver tissue, which enhanced both fibrosis and the relative protein expressions of the TGF-β pathway. Moreover, YB-1 overexpression promoted HSC activation in response to TGF-β1 stimulation, but its knockdown inhibited liver fibrosis in vitro. Both in vitro and in vivo experiments indicated the expression of TGF-β3 in the YB-1 overexpression group to be suppressed, and liver fibrosis was more obvious in the YB-1-overexpression group than in the YB-1-inhibition group. YB-1 attenuated TGF-β3 transcription by binding to its promoter, which is involved in the effect of YB-1 on liver fibrosis.
Conclusions: YB-1 overexpression in HSCs promoted liver fibrosis by attenuating TGF-β3 transcription.
Keywords: Hepatic stellate cell (HSC); Y-box binding protein 1 (YB-1); liver fibrosis; transforming growth factor-beta 3 (TGF-β3).
2023 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://atm.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/atm-23-835/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Physalin D attenuates hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis by blocking TGF-β/Smad and YAP signaling.Phytomedicine. 2020 Nov;78:153294. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153294. Epub 2020 Jul 28. Phytomedicine. 2020. PMID: 32771890
-
Transforming growth factor beta-1 upregulates glucose transporter 1 and glycolysis through canonical and noncanonical pathways in hepatic stellate cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2021 Oct 28;27(40):6908-6926. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i40.6908. World J Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 34790014 Free PMC article.
-
Positive feedback loop of YB-1 interacting with Smad2 promotes liver fibrosis.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017 Mar 18;484(4):753-761. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.01.148. Epub 2017 Jan 30. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017. PMID: 28153731
-
Epigenetically-Regulated MicroRNA-9-5p Suppresses the Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells via TGFBR1 and TGFBR2.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;43(6):2242-2252. doi: 10.1159/000484303. Epub 2017 Oct 27. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 29073595
-
MicroRNA-30 Protects Against Carbon Tetrachloride-induced Liver Fibrosis by Attenuating Transforming Growth Factor Beta Signaling in Hepatic Stellate Cells.Toxicol Sci. 2015 Jul;146(1):157-69. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfv081. Epub 2015 Apr 24. Toxicol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25912033
Cited by
-
YBX1/CD36 positive feedback loop-mediated lipid accumulation drives metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease.Int J Biol Sci. 2025 Feb 18;21(5):2118-2134. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.105798. eCollection 2025. Int J Biol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40083711 Free PMC article.
-
TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway in fatty liver disease: a case-control study.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Oct 1;51(1):1031. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-09973-w. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39352573
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
