Promotion of liver fibrosis by Y-box binding protein 1 via the attenuation of transforming growth factor-beta 3 transcription
- PMID: 37082693
- PMCID: PMC10113103
- DOI: 10.21037/atm-23-835
Promotion of liver fibrosis by Y-box binding protein 1 via the attenuation of transforming growth factor-beta 3 transcription
Abstract
Background: Spurred by the seriousness of liver fibrosis, we evaluated the correlation between Y-box binding protein 1 (YB-1) and transforming growth factor-beta 3 (TGF-β3) expression levels in the signaling pathways of the disease.
Methods: Based on a mouse model of carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis, YB-1 overexpression lentivirus was used to explore the effect of YB-1 on liver fibrosis in vivo. In addition, a hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation model in the HSC line LX-2 was developed using TGF-β1. Western blot assays were used to investigate the effects of YB-1 overexpression and knockdown on liver fibrosis. Finally, chromatin immunoprecipitation and luciferase reporter assays were used to elucidate the relationship between YB-1 and its downstream signaling pathways.
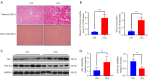
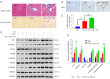
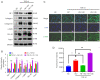
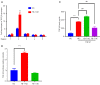
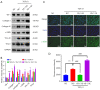
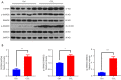
Results: YB-1 was overexpressed in fibrotic liver tissue, which enhanced both fibrosis and the relative protein expressions of the TGF-β pathway. Moreover, YB-1 overexpression promoted HSC activation in response to TGF-β1 stimulation, but its knockdown inhibited liver fibrosis in vitro. Both in vitro and in vivo experiments indicated the expression of TGF-β3 in the YB-1 overexpression group to be suppressed, and liver fibrosis was more obvious in the YB-1-overexpression group than in the YB-1-inhibition group. YB-1 attenuated TGF-β3 transcription by binding to its promoter, which is involved in the effect of YB-1 on liver fibrosis.
Conclusions: YB-1 overexpression in HSCs promoted liver fibrosis by attenuating TGF-β3 transcription.
Keywords: Hepatic stellate cell (HSC); Y-box binding protein 1 (YB-1); liver fibrosis; transforming growth factor-beta 3 (TGF-β3).
2023 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://atm.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/atm-23-835/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
