Salt Restriction and Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitor Improve the Responsiveness of the Small Artery in Salt-Sensitive Hypertension
- PMID: 37082725
- PMCID: PMC10110468
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.79741
Salt Restriction and Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitor Improve the Responsiveness of the Small Artery in Salt-Sensitive Hypertension
Abstract
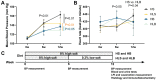
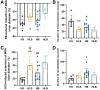
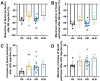
For salt-sensitive hypertension (SSH), salt restriction and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors are essential treatments, but their effect on the function of resistance arteries is unclear. Here, we present an intravital study to detect the effect of salt restriction and ACE inhibitors on the function of the mesenteric small artery (MSA) in SSH. Dahl salt-sensitive rats were randomized into the following groups: ACE inhibitor gavage, salt restriction, ACE inhibitor combined with salt restriction, and high-salt diet. After a 12-week intervention, the mesenteric vessels maintained their perfusion in vivo, and the changes in the diameter and blood perfusion of the MSAs to norepinephrine (NE) and acetylcholine (ACh) were detected. Switching from a high-salt diet to a low-salt diet (i.e., salt restriction) attenuated the vasoconstriction of the MSAs to NE and promoted the vasodilatation to ACh, while ACE inhibitor improved the vasodilatation more obviously. Pathologically, changes in local ACE, AT1R, and eNOS expression were involved in these processes induced by a high-salt diet. Our study suggests that salt restriction and ACE inhibitor treatment improve high salt intake-induced MSA dysfunction in SSH, and salt restriction is a feasible and effective treatment. Our findings may provide a scientific basis for the treatment of hypertension.
Keywords: Hypertension; angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor; mesenteric small artery; salt intake; salt restriction; vascular reactivity.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Unger T, Borghi C, Charchar F, Khan NA, Poulter NR, Prabhakaran D. et al. 2020 International Society of Hypertension global hypertension practice guidelines. Journal of hypertension. 2020;38:982–1004. - PubMed
-
- Rust P, Ekmekcioglu C. Impact of Salt Intake on the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Hypertension. In: Islam MS, editor. Hypertension: from basic research to clinical practice. Cham: Springer International Publishing. 2017. p. 61-84. - PubMed
-
- He FJ, Tan M, Ma Y, Macgregor GA. Salt Reduction to Prevent Hypertension and Cardiovascular Disease. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2020;75:632–47. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

