USP14 promotes the malignant progression and ibrutinib resistance of mantle cell lymphoma by stabilizing XPO1
- PMID: 37082728
- PMCID: PMC10110470
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.80467
USP14 promotes the malignant progression and ibrutinib resistance of mantle cell lymphoma by stabilizing XPO1
Abstract
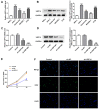
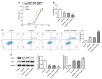
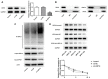
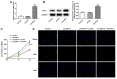
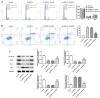
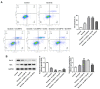
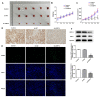
Background: Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) is a heterogeneous disease belonging to non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. In recent years, the morbidity rate of MCL is ascending, and the prognosis remains unfavorable. Ubiquitin-specific proteases14 (USP14) has been evidenced to be engaged in the process of malignant tumors. In this article, the role of USP14 in the malignant process of MCL and the mechanism of ibrutinib resistance were discussed. Methods: Through qRT-PCR and western blot, the mRNA and protein expressions of USP14 in MCL cells were tested. USP14 interference plasmid was constructed by cell transfection technology, and then CCK8 and EdU assays were applied to appraise cell proliferation. Cell cycle and cell apoptosis were estimated by flow cytometry and western blot. The sensitivity of MCL cells to ibrutinib was also investigated. Next, western blot, co-IP, Cycloheximide (CHX) assay and other techniques were used to detect the relationship between USP14 and XPO1. Finally, by simultaneously inhibiting USP14 and overexpressing XPO1, the impacts of USP14 on the malignant process of MCL and the regulatory mechanism of ibrutinib sensitivity in MCL were discussed. Results: USP14 expression was markedly fortified in MCL cell lines. Interference of USP14 suppressed MCL cell viability, potentiated cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, and ibrutinib sensitivity. This process might be achieved by USP14 deubiquitination through enhancing XPO1 stability. Conclusion: USP14 can promote the malignant progression and ibrutinib sensitivity of MCL by stabilizing XPO1.
Keywords: MCL; USP14; XPO1; ibrutinib resistance; ubiquitination.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CDKN1C-mediated growth inhibition by an EZH1/2 dual inhibitor overcomes resistance of mantle cell lymphoma to ibrutinib.Cancer Sci. 2021 Jun;112(6):2314-2324. doi: 10.1111/cas.14905. Epub 2021 May 1. Cancer Sci. 2021. PMID: 33792119 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of MYC, a bona fide client of HSP90, contributes to intrinsic ibrutinib resistance in mantle cell lymphoma.Blood Adv. 2018 Aug 28;2(16):2039-2051. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2018016048. Blood Adv. 2018. PMID: 30115641 Free PMC article.
-
CCND1 mutations increase protein stability and promote ibrutinib resistance in mantle cell lymphoma.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 8;7(45):73558-73572. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12434. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27713153 Free PMC article.
-
Ibrutinib resistance in mantle cell lymphoma: clinical, molecular and treatment aspects.Br J Haematol. 2018 May;181(3):306-319. doi: 10.1111/bjh.15108. Epub 2018 Jan 23. Br J Haematol. 2018. PMID: 29359797 Review.
-
Cell Cycle Dysregulation in Mantle Cell Lymphoma: Genomics and Therapy.Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2020 Oct;34(5):809-823. doi: 10.1016/j.hoc.2020.05.003. Epub 2020 Aug 1. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2020. PMID: 32861279 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
USP14 exhibits high expression levels in hepatocellular carcinoma and plays a crucial role in promoting the growth of liver cancer cells through the HK2/AKT/P62 axis.BMC Cancer. 2024 Feb 21;24(1):237. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12009-y. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38383348 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin-specific peptidase 14 promotes neuron injury by stabilizing acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 4 through deubiquitination.Cytojournal. 2025 Feb 5;22:11. doi: 10.25259/Cytojournal_52_2024. eCollection 2025. Cytojournal. 2025. PMID: 40134566 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dreyling M, Kluin-Nelemans HC, Bea S, Klapper W, Vogt N, Delfau-Larue MH. et al. Update on the molecular pathogenesis and clinical treatment of mantle cell lymphoma: report of the 11th annual conference of the European Mantle Cell Lymphoma Network. Leuk Lymphoma. 2013;54:699–707. - PubMed
-
- Condoluci A, Rossi D, Zucca E, Cavalli F. Toward a Risk-Tailored Therapeutic Policy in Mantle Cell Lymphoma. Curr Oncol Rep. 2018;20:79. - PubMed
-
- Vose JM. Mantle cell lymphoma: 2017 update on diagnosis, risk-stratification, and clinical management. Am J Hematol. 2017;92:806–13. - PubMed
-
- Grimm KE, O'Malley DP. Aggressive B cell lymphomas in the 2017 revised WHO classification of tumors of hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2019;38:6–10. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

