Farnesoid X receptor is inhibited after ileum transposition in diabetic rats: its hypoglycemic effect
- PMID: 37082732
- PMCID: PMC10110471
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.80563
Farnesoid X receptor is inhibited after ileum transposition in diabetic rats: its hypoglycemic effect
Abstract
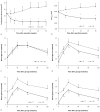
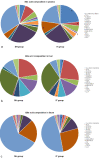
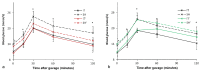
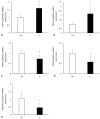
Background: Aim to investigate bile acid profile changes and the Farnesoid X receptor (FXR) status after ileotransposition (IT), and reveal its possible hypoglycemic mechanism. Methods: Twenty male diabetic rats were randomly assigned into the IT group and the sham IT (SH) group. Bile acid profiles were measured using an ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Glucose metabolism was monitored after oral administration of FXR inhibitor and agonist. And the expression of key FXR target genes were measured. Results: The levels of β-muricholic acid (P = 0.047), tauro-α-muricholic acid and tauro-β-muricholic acid (P < 0.001) in plasma in the IT group were higher than those in the SH group, and the levels of taurocholic acid (P = 0.049) and turoursodeoxycholic acid (P = 0.030) were lower than those in the SH group. After inhibition of intestinal FXR, the glucose metabolism in the SH group was improved. When FXR agonist was given, the blood glucose level was increased in both groups. After sacrifice, the levels of glycoursodeoxycholic acid, tauro-α-muricholic acid and tauro-β-muricholic acid in liver and ileum tissues were higher than those in the SH group (P < 0.05), the level of α- muricholic acid (P < 0.001) in liver tissues were lower than that in the SH group. Moreover, the expression of CYP7A1 mRNA (P < 0.001) and FGF15 mRNA (P = 0.001) in the IT group was significantly higher, and the expression of PEPCK mRNA (P = 0.004), SREPB1c mRNA (P = 0.005) and SRB1 mRNA (P = 0.001) were significantly lower than that in the SH group. Conclusions: We demonstrate a remarkable heterogeneity of BA profiles after IT, FXR activation might has a detrimental effect on glucose metabolism.
Keywords: bile acids and salts; diabetes mellitus; farnesoid X receptor; glucose; ileum.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The water extract of Radix scutellariae, its total flavonoids and baicalin inhibited CYP7A1 expression, improved bile acid, and glycolipid metabolism in T2DM mice.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Jul 15;293:115238. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115238. Epub 2022 Mar 26. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35351576
-
Polyphenol-induced improvements in glucose metabolism are associated with bile acid signaling to intestinal farnesoid X receptor.BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2020 Aug;8(1):e001386. doi: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2020-001386. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2020. PMID: 32771984 Free PMC article.
-
Jingangteng capsules ameliorate liver lipid disorders in diabetic rats by regulating microflora imbalances, metabolic disorders, and farnesoid X receptor.Phytomedicine. 2024 Sep;132:155806. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155806. Epub 2024 Jun 4. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38876009
-
Gut microbiota regulates bile acid metabolism by reducing the levels of tauro-beta-muricholic acid, a naturally occurring FXR antagonist.Cell Metab. 2013 Feb 5;17(2):225-35. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2013.01.003. Cell Metab. 2013. PMID: 23395169
-
Bile acid signaling in lipid metabolism: metabolomic and lipidomic analysis of lipid and bile acid markers linked to anti-obesity and anti-diabetes in mice.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Jan;1851(1):19-29. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2014.04.008. Epub 2014 May 4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 24796972 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Bile salt signaling and bile salt-based therapies in cardiometabolic disease.Clin Sci (Lond). 2024 Jan 10;138(1):1-21. doi: 10.1042/CS20230934. Clin Sci (Lond). 2024. PMID: 38180064 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Safiri S, Karamzad N, Kaufman JS, Bell AW, Nejadghaderi SA, Sullman MJM. et al. Prevalence, Deaths and Disability-Adjusted-Life-Years (DALYs) Due to Type 2 Diabetes and Its Attributable Risk Factors in 204 Countries and Territories, 1990-2019: Results From the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2022;13:838027. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahn CH, Choi EH, Oh TJ, Cho YM. Ileal Transposition Increases Pancreatic beta Cell Mass and Decreases beta Cell Senescence in Diet-Induced Obese Rats. Obes Surg. 2020;30:1849–58. - PubMed
-
- Cohen R, Caravatto PP, Petry TZ. Innovative metabolic operations. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2016;12:1247–55. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

