Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review of the Qualitative Studies
- PMID: 37082898
- PMCID: PMC10236425
- DOI: 10.1177/10732748231168318
Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review of the Qualitative Studies
Abstract
Objective: Quality of life (QoL) in breast cancer patients is still an important topic. Despite numerous quantitative scales, qualitative studies can help to in-depth understand the QoL of breast cancer patients. The purpose of this systematic review was to integrate qualitative studies on the QoL of women with breast cancer.
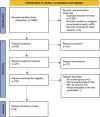
Methods: A literature search was performed in electronic databases including PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science from January 1, 2010 until June 28, 2022 to find out qualitative studies assessing breast cancer patient's QoL. Two authors independently evaluated methodological quality according to the consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ) checklist. Data were extracted and reported by themes for cancer-free women and patients with metastatic cancer separately.
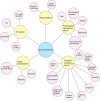
Results: In all, 1565 citations were retrieved. After removing 1387 duplicate and irrelevant papers, the full texts of 27 articles were reviewed and finally, 9 were eligible for evaluation. In quality checking of the citations, all articles gained the required quality score. After examining and merging similar topics, nine major themes were extracted. Physical, spiritual, and psychological aspects of QoL were the common issues in cancer-free women (before and after the COVID-19 pandemic) and patients with metastatic cancer. Perception of cancer and social life were the other main concerns in cancer-free women, whereas, in metastatic patients' overall survival and planning for the future and their children's life was the focus of interest. Women with metastatic disease showed more vulnerability in coping compared to cancer-free women.
Conclusion: This review provides an opportunity to have a closer look into the several domains of QoL in women with breast cancer. In-depth information provided by this review might help to develop interventions for patients and their families to support women to cope much better with their life challenges.
Keywords: breast cancer; qualitative study; quality of life.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al.Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71. - PubMed
-
- Krigel S, Myers J, Befort C, Krebill H, Klemp J. ‘Cancer changes everything!’ Exploring the lived experiences of women with metastatic breast cancer. Int J Palliat Nurs. 2014;20(7):334-342. - PubMed
-
- Ng HS, Vitry A, Koczwara B, Roder D, McBride ML. Patterns of comorbidities in women with breast cancer: A Canadian population-based study. Cancer Causes Control. 2019;30(9):931-941. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical