Establishing Novel Antiretroviral Imaging for Hair to Elucidate Nonadherence: Protocol for a Single-Arm Cross-sectional Study
- PMID: 37083754
- PMCID: PMC10163405
- DOI: 10.2196/41188
Establishing Novel Antiretroviral Imaging for Hair to Elucidate Nonadherence: Protocol for a Single-Arm Cross-sectional Study
Abstract
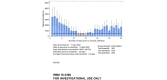
Background: Adherence to antiretroviral (ARV) therapy is critical for achieving HIV RNA suppression in people living with HIV and for preventing HIV infection in uninfected individuals using preexposure prophylaxis. However, a high level of adherence can be challenging to achieve for people living with HIV on lifelong ARVs and for HIV-negative individuals using daily preexposure prophylaxis who are not at daily risk for HIV infection. Current biological measures of adherence are invasive and use bioanalytical methods that do not allow for real-time feedback during a clinic visit. This study was designed to test the feasibility and acceptability of using MedViewer, a novel, minimally invasive, hair-based assay that measures longitudinal ARV drug adherence in real time and provides an output for provider-patient discussion.
Objective: The primary objectives were to investigate the feasibility of delivering the MedViewer results as planned, the acceptability of participation in a discussion of the MedViewer results, and the appropriateness of using MedViewer for adherence counseling. The secondary objectives were to investigate additional dimensions of feasibility, acceptability, and appropriateness of using the MedViewer test during a routine clinic visit for people with HIV.
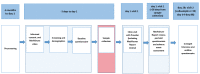
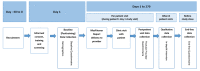
Methods: The proposed study was a single-arm cross-sectional study among patients receiving HIV care and providers of HIV care in a southeastern infectious disease clinic. The study originally planned to implement the MedViewer test with 50 eligible patients who were living with HIV across 2 viral load strata (undetectable or detectable plasma HIV RNA over the previous 2 years), administer brief visit-specific questionnaires to all patient and provider participants, and conduct qualitative in-depth interviews and quantitative end-line questionnaires with a subsample of patient participants (n=30) and all provider participants.
Results: The Establishing Novel Antiretroviral Imaging for Hair to Elucidate Nonadherence study was funded by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases and approved by the local institutional review board on November 4, 2019. Provider participant enrollment began on January 17, 2020, and patient participant enrollment began on January 22, 2020. Participant enrollment was halted on March 16, 2020, because of the COVID-19 pandemic (16 providers and 10 patients on study). Study activities resumed on February 2, 2021, with COVID-19 modifications approved by the local institutional review board. Participant enrollment closed on October 8, 2021, and data collection closed on November 15, 2021. In total, 36 unique patient participants, representing 37 samples, and 20 provider participants were enrolled. Data analysis and manuscript writing will take place throughout 2023.
Conclusions: We anticipate that the data collected through this study will provide important insights regarding the feasibility, acceptability, and appropriateness of incorporating new real-time longitudinal, minimally invasive adherence tests into routine clinical care and identify potential barriers to medication adherence among patients.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT04232540; https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04232540.
International registered report identifier (irrid): RR1-10.2196/41188.
Keywords: AIDS; HIV; IR-MALDESI; adherence; antiretroviral therapy; hair; infrared matrix–assisted laser desorption electrospray ionization.
©Amanda Poliseno, Ella Ferguson, Rose Perry, Alexandra Munson, Alexandra Davis, Lauren Hill, Jessica Keys, Nicole White, Claire Farel, Cynthia Gay, Carol Golin, Elias Rosen, Angela Kashuba. Originally published in JMIR Research Protocols (https://www.researchprotocols.org), 21.04.2023.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures

References
-
- HIV/AIDS treatment guidelines. Clinical info. [2022-02-14]. https://clinicalinfo.hiv.gov/en/guidelines .
-
- Gilliland Jr WM, Prince HM, Poliseno A, Kashuba AD, Rosen EP. Infrared matrix-assisted laser desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry imaging of human hair to characterize longitudinal profiles of the antiretroviral maraviroc for adherence monitoring. Anal Chem. 2019 Aug 20;91(16):10816–22. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.9b02464. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/31345022 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baxi SM, Liu A, Bacchetti P, Mutua G, Sanders EJ, Kibengo FM, Haberer JE, Rooney J, Hendrix CW, Anderson PL, Huang Y, Priddy F, Gandhi M. Comparing the novel method of assessing PrEP adherence/exposure using hair samples to other pharmacologic and traditional measures. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2015 Jan 01;68(1):13–20. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000000386. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/25296098 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Adams JL, Sykes C, Menezes P, Prince HM, Patterson KB, Fransen K, Crucitti T, De Baetselier I, Van Damme L, Kashuba AD. Tenofovir diphosphate and emtricitabine triphosphate concentrations in blood cells compared with isolated peripheral blood mononuclear cells: a new measure of antiretroviral adherence? J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2013 Mar 01;62(3):260–6. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e3182794723. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/23111578 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

