The mechanism of peach kernel and safflower herb-pair for the treatment of liver fibrosis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking technology: A review
- PMID: 37083803
- PMCID: PMC10118378
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000033593
The mechanism of peach kernel and safflower herb-pair for the treatment of liver fibrosis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking technology: A review
Abstract
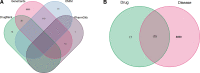
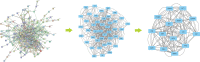
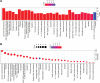
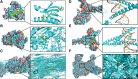
Peach kernel and safflower herb-pair (PKSH) are widely used in traditional Chinese medicine for the treatment of liver fibrosis. Therefore, network pharmacology was performed to explore potential therapeutic targets and pharmacological mechanisms of PKSH. The active components of PKSH from the Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology Database and Analysis Platform database and potential targets of liver fibrosis from the Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man, Pharmacogenetics and Pharmacogenomics Knowledge Base, GeneCards, and DrugBank Database were identified. The protein-protein interaction network was constructed using Cytoscape (v3.8.0). Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway enrichment analyses were performed for the treatment of liver fibrosis, and molecular docking was carried out to verify the results of network pharmacology analysis. After screening disease-related genes, 179 intersection genes overlapped between 196 target proteins of the active compound and 9189 potential disease targets. Furthermore, we obtained 15 hub nodes and 146 edges to establish a related network diagram using CytoNCA. 2559 Gene Ontology biological processes underlying PKSH have been explored for the treatment of liver fibrosis, in which the response to oxidative stress plays a vital role. Furthermore, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes enrichment analysis revealed that PKSH might play a role in inhibiting liver fibrosis, mainly through the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. PKSH can regulate the response to oxidative stress through the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway for the treatment of liver fibrosis. The main bioactive components in PKSH, including quercetin and luteolin, can activate the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway by binding with the hub targets of the disease, which may provide insights into drug development for liver fibrosis.
Copyright © 2023 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Potential Molecular Mechanisms of Ephedra Herb in the Treatment of Nephrotic Syndrome Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Jul 5;2022:9214589. doi: 10.1155/2022/9214589. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35837376 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-cervical cancer effects of Compound Yangshe granule through the PI3K/AKT pathway based on network pharmacology.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Jan 30;301:115820. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115820. Epub 2022 Oct 8. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36220511
-
Integration of Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Technology Reveals the Mechanism of the Therapeutic Effect of Xixin Decoction on Alzheimer's Disease.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2022;25(10):1785-1804. doi: 10.2174/1386207325666220523151119. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2022. PMID: 35616676
-
Exploration of the potential mechanism of Yiyi Tongfeng Formula in the treatment of acute gouty arthritis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking: A review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Sep 13;103(37):e39609. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039609. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39287271 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Network pharmacology and molecular docking approaches predict the mechanisms of Corididius chinensis in treating manganese-induced nervous system diseases: A review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Oct 27;102(43):e35669. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000035669. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37904435 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Erjingwan and Alzheimer's disease: research based on network pharmacology and experimental confirmation.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Apr 29;15:1328334. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1328334. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38741585 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of potential biomarkers from amino acid transporter in the activation of hepatic stellate cells via bioinformatics.Front Genet. 2024 Dec 4;15:1499915. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1499915. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 39698464 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical intervention effect of Xuefu Zhuyu decoction on chronic heart failure complicated with depression.World J Psychiatry. 2024 Jun 19;14(6):857-865. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v14.i6.857. eCollection 2024 Jun 19. World J Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38984345 Free PMC article.
-
Network pharmacology and molecular docking technology for exploring the effect and mechanism of Radix Bupleuri and Radix Paeoniae Alba herb-pair on anti-hepatitis: A review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Dec 1;102(48):e35443. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000035443. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 38050220 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic diversity, clinical uses, and phytochemical and pharmacological properties of safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.): an important medicinal plant.Front Pharmacol. 2024 May 10;15:1374680. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1374680. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38799156 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schuppan D, Ashfaq-Khan M, Yang AT, et al. . Liver fibrosis: direct antifibrotic agents and targeted therapies. Matrix Biol. 2018;68-69:435–51. - PubMed
-
- Ricco G, Coco B, Colombatto P, et al. . Highly dynamic changes of regional HBV epidemiology over two decades. Dig Liver Dis. 2022;S1590-8658:00779-4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

