Vitamin D Supplementation and Muscle Power, Strength and Physical Performance in Older Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 37084814
- PMCID: PMC10447505
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajcnut.2023.04.021
Vitamin D Supplementation and Muscle Power, Strength and Physical Performance in Older Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to 'Vitamin D Supplementation and Muscle Power, Strength and Physical Performance in Older Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial' [The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, Volume 117, Issue 6, June 2023, Pages 1086-1095].Am J Clin Nutr. 2023 Aug;118(2):486. doi: 10.1016/j.ajcnut.2023.06.004. Epub 2023 Jun 15. Am J Clin Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37331702 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Low 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) concentrations (<30 ng/mL [<50 nmol/L]) have been associated with muscle weakness and impaired physical performance in observational studies. However, the effect of vitamin D supplementation on changes in muscle strength and physical performance in randomized controlled trials has been mixed.
Objectives: To determine the effect of daily vitamin D supplementation on leg power, strength, and physical performance in low-functioning older adults with 25(OH)D concentrations of 18 to <30 ng/mL.
Methods: In this double-blind, randomized controlled trial, 136 low-functioning [Short Physical Performance Battery (SPPB) scores ≤10] adults aged 65-89 y with 25(OH)D concentrations of 18 to <30 ng/mL were randomly assigned to 2000 IU/d vitamin D3 or placebo for 12 mo. Lower-extremity leg power (primary outcome), leg and grip strength, SPPB, timed up and go (TUG), postural sway, and gait velocity and spatiotemporal parameters (secondary outcomes) were assessed at baseline, 4 and 12 mo. A subset (n = 37) also underwent a muscle biopsy at baseline and 4 mo and muscle fiber composition and contractile properties were assessed.
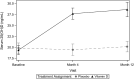
Results: Participants' mean ± SD age and SPPB scores at baseline were 73.4 ± 6.3 y and 7.8 ± 1.8, respectively. Mean ± SD 25(OH)D concentrations at baseline and 12 mo were 19.4 ± 4.2 ng/mL and 28.6 ± 6.7 ng/mL in the vitamin D group and 19.9 ± 4.9 ng/mL and 20.2 ± 5.0 ng/mL in the placebo group for a mean ± SE difference of 9.1 ± 1.1 ng/mL (P < 0.0001). However, there were no differences in change in leg power, leg or grip strength, SPPB score, TUG, postural sway, or gait velocity and spatiotemporal parameters by intervention group over 12 mo or muscle fiber composition and contractile properties over 4 mo.
Conclusions: In low-functioning older adults with 25(OH)D concentrations of 18 to <30 ng/mL, randomization to 2000 IU/d vitamin D3 did not result in improvements in leg power, strength, or physical performance or muscle fiber composition and contractile properties. This trial was registered at clinicaltrials.gov as NCT02015611.
Keywords: leg power; older adults; physical performance; strength; vitamin D.
Copyright © 2023 American Society for Nutrition. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Janssen I., Heymsfield S.B., Ross R. Low relative skeletal muscle mass (sarcopenia) in older persons is associated with functional impairment and physical disability. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2002;50(5):889–896. - PubMed
-
- Visser M., Goodpaster B.H., Kritchevsky S.B., Newman A.B., Nevitt M., Rubin S.M., et al. Muscle mass, muscle strength, and muscle fat infiltration as predictors of incident mobility limitations in well-functioning older persons. J. Gerontol. A. Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2005;60(3):324–333. - PubMed
-
- Dawson-Hughes B. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and functional outcomes in the elderly. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008;88(2):537S–540S. - PubMed
-
- Ceglia L., Harris S.S. Vitamin D and its role in skeletal muscle, Calcif. Tissue Int. 2013;92(2):151–162. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

