Genetic Moderation of the Association of β-Amyloid With Cognition and MRI Brain Structure in Alzheimer Disease
- PMID: 37085326
- PMCID: PMC10351305
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000207305
Genetic Moderation of the Association of β-Amyloid With Cognition and MRI Brain Structure in Alzheimer Disease
Abstract
Background and objectives: There is considerable heterogeneity in the association between increasing β-amyloid (Aβ) pathology and early cognitive dysfunction in preclinical Alzheimer disease (AD). At this stage, some individuals show no signs of cognitive dysfunction, while others show clear signs of decline. The factors explaining this heterogeneity are particularly important for understanding progression in AD but remain largely unknown. In this study, we examined an array of genetic variants that may influence the relationships among Aβ, brain structure, and cognitive performance in 2 large cohorts.
Methods: In 2,953 cognitively unimpaired participants from the Anti-Amyloid Treatment in Asymptomatic Alzheimer disease (A4) study, interactions between genetic variants and 18F-Florbetapir PET standardized uptake value ratio (SUVR) to predict the Preclinical Alzheimer Cognitive Composite (PACC) were assessed. Genetic variants identified in the A4 study were evaluated in the Alzheimer Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI, N = 527) for their association with longitudinal cognition and brain atrophy in both cognitively unimpaired participants and those with mild cognitive impairment.
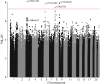
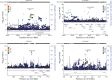
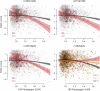
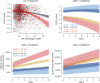
Results: In the A4 study, 4 genetic variants significantly moderated the association between Aβ load and cognition. Minor alleles of 3 variants were associated with additional decreases in PACC scores with increasing Aβ SUVR (rs78021285, β = -2.29, SE = 0.40, p FDR = 0.02, nearest gene ARPP21; rs71567499, β = -2.16, SE = 0.38, p FDR = 0.02, nearest gene PPARD; and rs10974405, β = -1.68, SE = 0.29, p FDR = 0.02, nearest gene GLIS3). The minor allele of rs7825645 was associated with less decrease in PACC scores with increasing Aβ SUVR (β = 0.71, SE = 0.13, p FDR = 0.04, nearest gene FGF20). The genetic variant rs76366637, in linkage disequilibrium with rs78021285, was available in both the A4 and ADNI. In the A4, rs76366637 was strongly associated with reduced PACC scores with increasing Aβ SUVR (β = -1.01, SE = 0.21, t = -4.90, p < 0.001). In the ADNI, rs76366637 was associated with accelerated cognitive decline (χ2 = 15.3, p = 0.004) and atrophy over time (χ2 = 26.8, p < 0.001), with increasing Aβ SUVR.
Discussion: Patterns of increased cognitive dysfunction and accelerated atrophy due to specific genetic variation may explain some of the heterogeneity in cognition in preclinical and prodromal AD. The genetic variant near ARPP21 associated with lower cognitive scores in the A4 and accelerated cognitive decline and brain atrophy in the ADNI may help to identify those at the highest risk of accelerated progression of AD.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Academy of Neurology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Amyloid and Tau Prediction of Cognitive and Functional Decline in Unimpaired Older Individuals: Longitudinal Data from the A4 and LEARN Studies.J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2024;11(4):802-813. doi: 10.14283/jpad.2024.122. J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2024. PMID: 39044488 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Association Between Apolipoprotein E ε2 vs ε4, Age, and β-Amyloid in Adults Without Cognitive Impairment.JAMA Neurol. 2021 Feb 1;78(2):229-235. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2020.3780. JAMA Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33044487 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Biomarker-Based Prediction of Longitudinal Tau Positron Emission Tomography in Alzheimer Disease.JAMA Neurol. 2022 Feb 1;79(2):149-158. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2021.4654. JAMA Neurol. 2022. PMID: 34928318 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding disease progression and improving Alzheimer's disease clinical trials: Recent highlights from the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative.Alzheimers Dement. 2019 Jan;15(1):106-152. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2018.08.005. Epub 2018 Oct 13. Alzheimers Dement. 2019. PMID: 30321505 Review.
-
Genetic studies of quantitative MCI and AD phenotypes in ADNI: Progress, opportunities, and plans.Alzheimers Dement. 2015 Jul;11(7):792-814. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2015.05.009. Alzheimers Dement. 2015. PMID: 26194313 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Integrating amyloid and tau imaging with proteomics and genomics in Alzheimer's disease.Cell Rep Med. 2024 Sep 17;5(9):101735. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101735. Cell Rep Med. 2024. PMID: 39293391 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disentangling genetic risks for development and progression of Alzheimer's disease.Brain. 2024 Aug 1;147(8):2604-2606. doi: 10.1093/brain/awae237. Brain. 2024. PMID: 39018494 Free PMC article.
-
Concomitant presence of a novel ARPP21 variant and CNVs in Chinese familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-frontotemporal dementia patients.Neurol Sci. 2025 Jan;46(1):195-205. doi: 10.1007/s10072-024-07759-3. Epub 2024 Sep 14. Neurol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39271636
