Microbial biomanufacturing for space-exploration-what to take and when to make
- PMID: 37085475
- PMCID: PMC10121718
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-37910-1
Microbial biomanufacturing for space-exploration-what to take and when to make
Abstract
As renewed interest in human space-exploration intensifies, a coherent and modernized strategy for mission design and planning has become increasingly crucial. Biotechnology has emerged as a promising approach to increase resilience, flexibility, and efficiency of missions, by virtue of its ability to effectively utilize in situ resources and reclaim resources from waste streams. Here we outline four primary mission-classes on Moon and Mars that drive a staged and accretive biomanufacturing strategy. Each class requires a unique approach to integrate biomanufacturing into the existing mission-architecture and so faces unique challenges in technology development. These challenges stem directly from the resources available in a given mission-class-the degree to which feedstocks are derived from cargo and in situ resources-and the degree to which loop-closure is necessary. As mission duration and distance from Earth increase, the benefits of specialized, sustainable biomanufacturing processes also increase. Consequentially, we define specific design-scenarios and quantify the usefulness of in-space biomanufacturing, to guide techno-economics of space-missions. Especially materials emerged as a potentially pivotal target for biomanufacturing with large impact on up-mass cost. Subsequently, we outline the processes needed for development, testing, and deployment of requisite technologies. As space-related technology development often does, these advancements are likely to have profound implications for the creation of a resilient circular bioeconomy on Earth.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
S.N.N. is an employee of Circe Bioscience Inc., a biomanufacturing company with financial interest in the microbiological production of foods. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
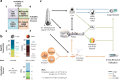
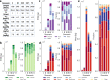
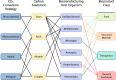
References
-
- Smith, M. et al. The artemis program: an overview of NASA’s activities to return humans to the moon. In 2020 IEEE Aerospace Conference, 1–10 (IEEE, 2020). https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9172323.
-
- Flores, G. et al. Deep space habitation: establishing a sustainable human presence on the moon and beyond. In 2021 IEEE Aerospace Conference (50100), 1–7 (IEEE, 2021). https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9438260.
-
- Creech, S., Guidi, J. & Elburn, D. Artemis: an overview of NASA’s activities to return humans to the moon. In IEEE Aerospace Conference (IEEE, Big Sky, MT, 2022). 10.1109/AERO53065.2022.9843277.
-
- Drake, B. G., Hoffman, S. J. & Beaty, D. W. Human exploration of Mars, design reference architecture 5.0. In Aerospace Conference, 2010 IEEE, 1–24 (IEEE, 2010). 10.1109/AERO.2010.5446736.
-
- Musk E. Making humans a multi-planetary species. New Space. 2017;5:46–61. doi: 10.1089/space.2017.29009.emu. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

