Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine encoding secreted non-stabilized spike in female mice
- PMID: 37085495
- PMCID: PMC10120480
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-37795-0
Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine encoding secreted non-stabilized spike in female mice
Abstract
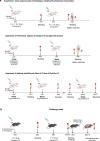
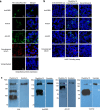
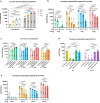
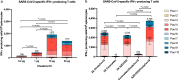
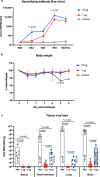
Establishment of an mRNA vaccine platform in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) is important to enhance vaccine accessibility and ensure future pandemic preparedness. Here, we describe the preclinical studies of "ChulaCov19", a SARS-CoV-2 mRNA encoding prefusion-unstabilized ectodomain spike protein encapsulated in lipid nanoparticles (LNP). In female BALB/c mice, ChulaCov19 at 0.2, 1, 10, and 30 μg elicits robust neutralizing antibody (NAb) and T cell responses in a dose-dependent relationship. The geometric mean titers (GMTs) of NAb against wild-type (WT, Wuhan-Hu1) virus are 1,280, 11,762, 54,047, and 62,084, respectively. Higher doses induce better cross-NAb against Delta (B.1.617.2) and Omicron (BA.1 and BA.4/5) variants. This elicited immunogenicity is significantly higher than those induced by homologous CoronaVac or AZD1222 vaccination. In a heterologous prime-boost study, ChulaCov19 booster dose generates a 7-fold increase of NAb against Wuhan-Hu1 WT virus and also significantly increases NAb response against Omicron (BA.1 and BA.4/5) when compared to homologous CoronaVac or AZD1222 vaccination. Challenge studies show that ChulaCov19 protects human-ACE-2-expressing female mice from COVID-19 symptoms, prevents viremia and significantly reduces tissue viral load. Moreover, anamnestic NAb response is undetectable in challenge animals. ChulaCov19 is therefore a promising mRNA vaccine candidate either as a primary or boost vaccination and has entered clinical development.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
DW, and MGA are named on patents that describe lipid nanoparticles for delivery of nucleic acid therapeutics, including mRNA and the use of modified mRNA in lipid nanoparticles as a vaccine platform. KR, DW, MGA, CK, EP, and SB are co-inventors of the submitted ChulaCov19 mRNA vaccine’s Patent. KL and JH are employees of Genevant Sciences Corporation and are named on patent describing lipid nanoparticles. WW is an employee of BioNet-Asia, Co. Ltd. We have disclosed those interests fully to their affiliations, and we have in place an approved plan for managing any potential conflicts arising from licensing of the patents. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

