Contribution of HIF-1α/BNIP3-mediated autophagy to lipid accumulation during irinotecan-induced liver injury
- PMID: 37085612
- PMCID: PMC10121580
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-33848-y
Contribution of HIF-1α/BNIP3-mediated autophagy to lipid accumulation during irinotecan-induced liver injury
Abstract
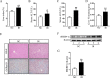
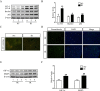
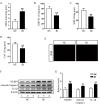
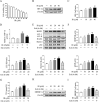
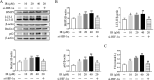
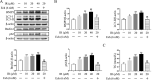
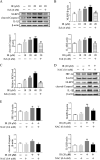
Irinotecan is a topoisomerase I inhibitor which has been widely used to combat several solid tumors, whereas irinotecan therapy can induce liver injury. Liver injury generally leads to tissue hypoxia, and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α), a pivotal transcription factor, mediates adaptive pathophysiological responses to lower oxygen condition. Previous studies have reported a relationship between HIF-1α and autophagy, and autophagy impairment is a common characteristic in a variety of diseases. Here, irinotecan (50 mg/kg) was employed on mice, and HepG2 and L-02 cells were cultured with irinotecan (10, 20 and 40 μM). In vivo study, we found that irinotecan treatment increased final liver index, serum aminotransferase level and hepatic lipid accumulation. Impaired autophagic flux and activation of HIF-1α/BNIP3 pathway were also demonstrated in the liver of irinotecan-treated mice. Moreover, irinotecan treatment significantly deteriorated hepatic oxidative stress, evidenced by increased MDA and ROS contents, as well as decreased GSH-Px, SOD and CAT contents. Interestingly, protein levels of NLRP3, cleaved-caspase 1 and IL-1β were enhanced in the liver of mice injected with irinotecan. In vitro study, irinotecan-treated HepG2 and L-02 cells also showed impaired autophagic flux, while HIF-1α inhibition efficaciously removed the accumulated autophagosomes induced by irinotecan. Additionally, irinotecan treatment aggravated lipid accumulation in HepG2 and L-02 cells, and HIF-1α inhibition reversed the effect of irinotecan. Furthermore, HIF-1α inhibition weakened irinotecan-induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation in HepG2 cells. Taken together, our results suggest that irinotecan induces liver injury by orchestrating autophagy via HIF-1α/BNIP3 pathway, and HIF-1α inhibition could alleviate irinotecan-induced lipid accumulation in HepG2 and L-02 cells, which will provide a new clue and direction for the prevention of side effects of clinical chemotherapy drugs.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

