Insulin effects on core neurotransmitter pathways involved in schizophrenia neurobiology: a meta-analysis of preclinical studies. Implications for the treatment
- PMID: 37085712
- PMCID: PMC10615753
- DOI: 10.1038/s41380-023-02065-4
Insulin effects on core neurotransmitter pathways involved in schizophrenia neurobiology: a meta-analysis of preclinical studies. Implications for the treatment
Abstract
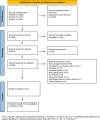
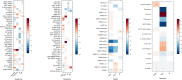
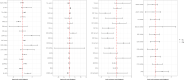
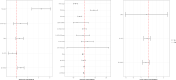
Impairment of insulin action and metabolic dysregulation have traditionally been associated with schizophrenia, although the molecular basis of such association remains still elusive. The present meta-analysis aims to assess the impact of insulin action manipulations (i.e., hyperinsulinemia, hypoinsulinemia, systemic or brain insulin resistance) on glutamatergic, dopaminergic, γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)ergic, and serotonergic pathways in the central nervous system. More than one hundred outcomes, including transcript or protein levels, kinetic parameters, and other components of the neurotransmitter pathways, were collected from cultured cells, animals, or humans, and meta-analyzed by applying a random-effects model and adopting Hedges'g to compare means. Two hundred fifteen studies met the inclusion criteria, of which 180 entered the quantitative synthesis. Significant impairments in key regulators of synaptic plasticity processes were detected as the result of insulin handlings. Specifically, protein levels of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) subunits including type 2A (NR2A) (Hedges' g = -0.95, 95%C.I. = -1.50, -0.39; p = 0.001; I2 = 47.46%) and 2B (NR2B) (Hedges'g = -0.69, 95%C.I. = -1.35, -0.02; p = 0.043; I2 = 62.09%), and Postsynaptic density protein 95 (PSD-95) (Hedges'g = -0.91, 95%C.I. = -1.51, -0.32; p = 0.003; I2 = 77.81%) were found reduced in insulin-resistant animal models. Moreover, insulin-resistant animals showed significantly impaired dopamine transporter activity, whereas the dopamine D2 receptor mRNA expression (Hedges'g = 3.259; 95%C.I. = 0.497, 6.020; p = 0.021; I2 = 90.61%) increased under insulin deficiency conditions. Insulin action modulated glutamate and GABA release, as well as several enzymes involved in GABA and serotonin synthesis. These results suggest that brain neurotransmitter systems are susceptible to insulin signaling abnormalities, resembling the discrete psychotic disorders' neurobiology and possibly contributing to the development of neurobiological hallmarks of treatment-resistant schizophrenia.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no competing interests. The authors have no financial or non-financial interests to disclose with regard to the content and aims of the study therein presented.
Figures


References
-
- Rummel-Kluge C, Komossa K, Schwarz S, Hunger H, Schmid F, Lobos CA, et al. Head-to-head comparisons of metabolic side effects of second generation antipsychotics in the treatment of schizophrenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Schizophr Res. 2010;123:225–33. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2010.07.012. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arranz B, Rosel P, Ramírez N, Dueñas R, Fernández P, Sanchez JM, et al. Insulin resistance and increased leptin concentrations in noncompliant schizophrenia patients but not in antipsychotic-naive first-episode schizophrenia patients. J Clin Psychiatry. 2004;65:1335–42. doi: 10.4088/JCP.v65n1007. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

