The association between childbirth-related fear, childbirth readiness, and fertility intentions, and childbirth readiness as the mediator
- PMID: 37085786
- PMCID: PMC10122374
- DOI: 10.1186/s12978-023-01607-x
The association between childbirth-related fear, childbirth readiness, and fertility intentions, and childbirth readiness as the mediator
Abstract
Background: Fertility intentions have been proved to be a reliable predictor of actual fertility behaviour. Also, childbirth-related fear (CBRF) has been proven to be negatively associated with childbirth readiness and fertility intentions among women, while childbirth readiness was positively related to fertility intentions. However, the associations and potential mechanisms between CBRF, childbirth readiness, and fertility intentions remain unknown. This study aimed to investigate the unique association between CBRF, childbirth readiness, and fertility intentions and whether childbirth readiness would mediate the relationship between CBRF and fertility intentions.
Method: A cross-sectional study of women (N = 1119, aged 16-53 years) who gave birth within 72 h was conducted. Using a convenience sampling, women were recruited from obstetric wards-10 comprehensive hospitals and 3 specialized hospitals in 7 provinces in mainland China. Pearson correlation was used to examine the relationship between CBRF, childbirth readiness, fertility intentions, and social support. Multivariate linear regression was further used to analyze the association between demographic and personal characteristics, CBRF, childbirth readiness, and fertility intentions. Mediation analysis was used to examine whether childbirth readiness mediates the relationship between CBRF and fertility intentions.
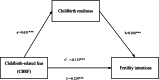
Results: Women with high childbirth readiness (β = 0.09, P = 0.002) had higher fertility intentions. However, women with high CBRF (β = - 0.17, P < 0.001) were more likely to have lower fertility intentions. CBRF had both direct and indirect effects on the level of fertility intentions. As predicted, childbirth readiness mediated the relationship between CBRF and the level of fertility intentions (estimate = - 0.012, 95% bootstrap CI: - 0.021 to - 0.005). Higher CBRF was associated with lower scores of childbirth readiness, which was associated with lower levels of fertility intentions.
Conclusions: This study established the evidence that CBRF had both direct and indirect effects on the level of fertility intentions and childbirth readiness mediated the relationship between CBRF and the level of fertility intentions. Specifically, higher CBRF was associated with lower scores of childbirth readiness, which was associated with lower levels of fertility intentions. This finding suggested that it is important for health policymakers and health providers to pay more attention to improving women's childbirth readiness, which might reduce the negative influence of CBRF on fertility intentions, thus strengthening their fertility intentions.
Keywords: Childbirth readiness; Childbirth-related fear; China; Fertility intentions; Mediator; Social support.
Plain language summary
Over the past two decades, fertility rates have been dropping steadily in most countries. Fertility intentions have been proven to be a reliable predictor of actual fertility behaviour. The worldwide sluggish fertility trend has brought about a series of issues, such as accelerated population ageing, shrinking workforce, and economic decline. China has the largest national population in the world, accounting for nearly one-fifth of the world's population, thus having a huge impact on global population trends. Therefore, in the context of significant fertility decline and population policy changes, timely research on fertility intention is of great significance for China and other low-fertility countries. CBRF has been proven to be negatively associated with childbirth readiness and fertility intentions among women, while childbirth readiness was positively related to fertility intentions. This study aimed to investigate the unique association between fertility intentions, CBRF, and childbirth readiness, and whether childbirth readiness would mediate the relationship between CBRF and fertility intentions. In this cross-sectional study, we found that women with high childbirth readiness had higher fertility intentions. However, women with high CBRF were more likely to have lower fertility intentions. Furthermore, CBRF had both direct and indirect effects on the level of fertility intentions. Childbirth readiness mediated the relationship between CBRF and the level of fertility intentions. Higher CBRF was associated with lower scores of childbirth readiness, which was associated with lower levels of fertility intentions. This finding suggested that it is important for health policymakers and health providers to pay more attention to improving women’s childbirth readiness, which might reduce the negative influence of CBRF on fertility intentions, thus strengthening their fertility intentions.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The influence of sense of coherence on psychological birth trauma: a parallel mediation model based on health Salutogenesis theory.Front Psychol. 2024 Jan 5;14:1320132. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1320132. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 38250100 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-cultural comparison of levels of childbirth-related fear in an Australian and Swedish sample.Midwifery. 2011 Aug;27(4):560-7. doi: 10.1016/j.midw.2010.05.004. Epub 2010 Jul 3. Midwifery. 2011. PMID: 20598787
-
Fertility Intentions, Parenting Attitudes, and Fear of Childbirth among College Students in China: A Cross-Sectional Study.J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2023 Feb;36(1):65-71. doi: 10.1016/j.jpag.2022.07.015. Epub 2022 Aug 3. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2023. PMID: 35933080
-
Interventions for fear of childbirth including tocophobia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Jul 7;7(7):CD013321. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013321.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34231203 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on women's fertility intentions and its policy implications for China and the rest of the world: a perspective essay.Biodemography Soc Biol. 2023 Apr-Sep;68(2-3):87-100. doi: 10.1080/19485565.2023.2221842. Epub 2023 Jun 12. Biodemography Soc Biol. 2023. PMID: 37309161 Review.
Cited by
-
Child abuse and experiences of discrimination are linked to fear of childbirth among younger patients in the US: a cohort study.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2025 Jul 9;25(1):735. doi: 10.1186/s12884-025-07841-4. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2025. PMID: 40634867 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction and unsupervised clustering of fertility intention among migrant workers based on machine learning: a cross-sectional survey from Henan, China.BMC Public Health. 2025 Jan 14;25(1):140. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-21412-4. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 39815227 Free PMC article.
-
Research on influencing factors of college teachers' second child fertility intentions--Taking Jinan as an example.PLoS One. 2024 May 21;19(5):e0299838. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0299838. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38771815 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of implementation of the WHO intrapartum care model on maternal and neonatal outcomes: a randomized control trial.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2024 Apr 17;24(1):283. doi: 10.1186/s12884-024-06449-4. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2024. PMID: 38632530 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Childbearing sense of coherence scale (CSOC-scale): development and validation.BMC Public Health. 2024 Jun 17;24(1):1613. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-19109-1. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38886687 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang H, Abbas KM, Abbasifard M, Abbasi-Kangevari M, Abbastabar H, Abd-Allah F, et al. Global age-sex-specific fertility, mortality, healthy life expectancy (HALE), and population estimates in 204 countries and territories, 1950–2019: a comprehensive demographic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet. 2020;396:1160–1203. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30977-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bloom D, Canning D, Fink G, Finlay J. The cost of low fertility in Europe. Eur J Popul. 2010;26:141–158. doi: 10.1007/s10680-009-9182-1. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous