De novo variation in EP300 gene cause Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome 2 in a Chinese family with severe early-onset high myopia
- PMID: 37085840
- PMCID: PMC10120144
- DOI: 10.1186/s12920-023-01516-9
De novo variation in EP300 gene cause Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome 2 in a Chinese family with severe early-onset high myopia
Abstract
Background: Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome (RSTS) is characterized by distinctive facial features, broad and often angulated thumbs and halluces, short stature, and moderate-to-severe intellectual disability, classified into two types RSTS1 (CREBBP-RSTS) and RSTS2 (EP300-RSTS). More often, the clinical features are inconclusive and the diagnosis of RSTS is established in a proband with identification of a heterozygous pathogenic variant in CREBBP or EP300 to confirm the diagnosis.
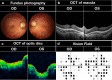
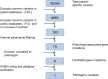
Methods: In this study, to describe an association between the clinical phenotype and the genotype of a RSTS2 patient who was initially diagnosed with severe early-onset high myopia (eoHM) from a healthy Chinese family, we tested the proband of this family by whole exome sequencing (WES) and further verified among other family members by Sanger sequencing. Real-time quantitative PCR was used to detect differences in the relative mRNA expression of candidate genes available in the proband and family members. Comprehensive ophthalmic tests as well as other systemic examinations were also performed on participants with various genotypes.
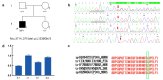
Results: Whole-exome sequencing revealed that the proband carried the heterozygous frameshift deletion variant c.3714_3715del (p.Leu1239Glyfs*3) in the EP300 gene, which was not carried by the normal parents and young sister as verified by Sanger sequencing, indicating that the variant was de novo. Real-time quantitative PCR showed that the mRNA expression of EP300 gene was lower in the proband than in other normal family members, indicating that such a variant caused an effect on gene function at the mRNA expression level. The variant was classified as pathogenic as assessed by the interpretation principles of HGMD sequence variants and ACMG guidelines. According to ACMG guidelines, the heterozygous frameshift deletion variant c.3714_3715del (p.Leu1239Glyfs*3) in the EP300 gene was more likely the pathogenic variant of this family with RSTS2.
Conclusions: Therefore, in this paper, we first report de novo heterozygous variation in EP300 causing eoHM-RSTS. Our study extends the genotypic spectrums for EP300-RSTS and better assists physicians in predicting, diagnosis, genetic counseling, eugenics guidance and gene therapy for EP300-RSTS.
Keywords: EP300 gene; Early onset high myopia; Phenotype; Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome 2.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
I declare that the authors have no competing interests as defined by Clinical Genetics or other interests that might be perceived to influence the results and discussion reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Skipping of Exon 20 in EP300: A Novel Variant Linked to Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome With Atypical and Severe Clinical Manifestations.Clin Genet. 2025 Mar;107(3):354-358. doi: 10.1111/cge.14654. Epub 2024 Nov 27. Clin Genet. 2025. PMID: 39603792 Free PMC article.
-
Case report: a Chinese girl like atypical Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome caused by a novel heterozygous mutation of the EP300 gene.BMC Med Genomics. 2023 Feb 16;16(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s12920-022-01424-4. BMC Med Genomics. 2023. PMID: 36797748 Free PMC article.
-
Rubinstein-Taybi 2 associated to novel EP300 mutations: deepening the clinical and genetic spectrum.BMC Med Genet. 2018 Mar 5;19(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s12881-018-0548-2. BMC Med Genet. 2018. PMID: 29506490 Free PMC article.
-
Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome with ganglioneuroblastoma: a case report and literature review.BMC Pediatr. 2025 Mar 31;25(1):253. doi: 10.1186/s12887-025-05608-6. BMC Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40159473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genotype-phenotype analysis of ocular findings in Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome - A case report and review of literature.Ophthalmic Genet. 2024 Feb;45(1):51-58. doi: 10.1080/13816810.2023.2196341. Epub 2023 Apr 5. Ophthalmic Genet. 2024. PMID: 37017262 Review.
Cited by
-
De novo variation in ARID1B gene causes Coffin-Siris syndrome 1 in a Chinese family with excessive early-onset high myopia.BMC Med Genomics. 2024 May 24;17(1):142. doi: 10.1186/s12920-024-01904-9. BMC Med Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38790056 Free PMC article.
-
Rubinstein Taybi syndrome caused by EP300 gene mutation: what we learned from two cases and literature review.Front Genet. 2025 Jul 2;16:1588657. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2025.1588657. eCollection 2025. Front Genet. 2025. PMID: 40672389 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stevens CA, Carey JC, Blackburn BL. Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome: a natural history study. A J Med Genet Suppl. 1990;6:30–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

