Development and validation of a risk score for predicting inconsistent condom use with women among men who have sex with men and women
- PMID: 37085861
- PMCID: PMC10120174
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-023-15672-1
Development and validation of a risk score for predicting inconsistent condom use with women among men who have sex with men and women
Abstract
Background: Men who have sex with men and women (MSMW) are the most important bridge population for HIV transmission. Condom use plays an important role for HIV infection. However the predictors for condom ues with females are not well characterized.
Methods: This was a cross-sectional study. Participants were enrolled by four community-based organizations (CBOs) by offline (bathrooms, bars), and online (gay applications, chat room) from April to December 2019. Electronic questionnare was fulfilled after a face-to-face training led by CBOs. We identified predictors of inconsistent condom use with females by creating a risk score based on regression coefficients. We externally validated this score via an independent cross-sectional survey conducted in Zhejiang Province in 2021. A total of 917, 615 MSMW were included in analysis in 2019 and 2021, seperately.
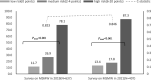
Results: Among 917 MSMW, 73.2% reported heterosexual behavior in the prior 6 months and 38.3% reported inconsistent condom use with females (ICUF) over that time. Compared with heterosexual/unsure MSMW, bisexual MSMW reported more male and female sex partners, higher proportion of inconsistent condom use with males, less commercial sex with males (p < 0.05). Four risky predictors of ICUF were identified: Duration of local residence ≦6 months; more than one male partner in the prior 6 months; inconsistent condom use with males in the prior 6 months; and never heard post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP). The proportions of respondents indicating ICUF in the low- (0), medium- (2-4) and high-risk (6-20) groups (according to our risk scoring system) were 11.7% (14/120), 26.9% (96/357), and 78.1% (125/160), respectively (Ptrend < 0.001). In the validation survey, the respective proportions of those reporting ICUF were 13.4% (15/112), 17.8% (24/185) and 87.3% (96/110) (Ptrend < 0.001).
Conclusions: We developed and validated a predictive risk score for ICUF among MSMW; four factors were identified, of which inconsistent condom use with men was the most important. Risk reduction intervention programs should focus on MSM who report inconsistent condom use with males, never heard PEP, having multiple partners and living in local less than 6 months.
Keywords: Bisexual; Factors; HIV; High risk sex.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Behavior and influencing factors of HIV infection among men who have sex with men only and men who have sex with both men and women in Shandong province].Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2019 Aug 10;40(8):941-946. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2019.08.013. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31484258 Chinese.
-
Sex hustling, injection drug use, and non-gay identification by men who have sex with men. Associations with high-risk sexual behaviors and condom use.Sex Transm Dis. 1998 Aug;25(7):353-60. doi: 10.1097/00007435-199808000-00006. Sex Transm Dis. 1998. PMID: 9713915
-
[The prevalence of HIV infection and sexual behaviors among men who have sex with men and women in Chengdu and Guangzhou, China].Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2012 Apr;33(4):368-73. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 22781407 Chinese.
-
Men Who Have Sex with Both Men and Women in West Africa: Factors Associated with a High Behavioral Risk of Acquiring HIV from Male Partners and Transmission to Women (CohMSM ANRS 12324-Expertise France).Arch Sex Behav. 2024 Feb;53(2):757-769. doi: 10.1007/s10508-023-02715-2. Epub 2023 Nov 16. Arch Sex Behav. 2024. PMID: 37973698 Free PMC article.
-
Condom use and risk factors of inconsistent or low use of the condoms during heterosexual anal intercourse in sub-Saharan Africa: a scoping review.Afr Health Sci. 2022 Mar;22(1):11-20. doi: 10.4314/ahs.v22i1.3. Afr Health Sci. 2022. PMID: 36032479 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Comparison of human immunodeficiency virus-related risky sexual behaviors between men who have sex with men only and men who have sex with men and women: A cross-sectional study in Eastern China.Prev Med Rep. 2024 Oct 30;48:102923. doi: 10.1016/j.pmedr.2024.102923. eCollection 2024 Dec. Prev Med Rep. 2024. PMID: 39555239 Free PMC article.
-
New sexually transmitted HIV infections from 2016 to 2050 in Guangdong Province, China: a study based on a dynamic compartmental model.BMC Public Health. 2024 May 14;24(1):1307. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-18735-z. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38745217 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous