The health and economic burden of musculoskeletal disorders in Belgium from 2013 to 2018
- PMID: 37085871
- PMCID: PMC10122398
- DOI: 10.1186/s12963-023-00303-z
The health and economic burden of musculoskeletal disorders in Belgium from 2013 to 2018
Abstract
Introduction: Low back pain (LBP), neck pain (NKP), osteoarthritis (OST) and rheumatoid arthritis (RHE) are among the musculoskeletal (MSK) disorders causing the greatest disability in terms of Years Lived with Disability. The current study aims to analyze the health and economic impact of these MSK disorders in Belgium, providing a summary of morbidity and mortality outcomes from 2013 to 2018, as well as direct and indirect costs from 2013 to 2017.
Methods: The health burden of LBP, NKP, OST and RHE in Belgium from 2013 to 2018 was summarized in terms of prevalence and disability-adjusted life years (DALY) using data from the Belgian health interview surveys (BHIS), the INTEGO database (Belgian registration network for general practitioners) and the Global Burden of Diseases study 2019. The economic burden included estimates of direct medical costs and indirect costs, measured by cost of work absenteeism. For this purpose, data of the respondents to the BHIS-2013 were linked with the national health insurance data (intermutualistic agency [IMA] database) 2013-2017.
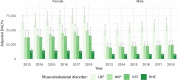
Results: In 2018, 2.5 million Belgians were affected by at least one MSK disorder. OST represented the disorder with the highest number of cases for both men and women, followed by LBP. In the same year, MSK disorders contributed to a total of 180,746 DALYs for female and 116,063 DALYs for men. LBP appeared to be the largest contributor to the health burden of MSK. Having at least one MSK disorder costed on average 3 billion € in medical expenses and 2 billion € in indirect costs per year, with LBP being the most costly.
Conclusion: MSK disorders represent a major health and economic burden in Belgium. As their burden will probably continue to increase in the future, acting on the risk factors associated to these disorders is crucial to mitigate both the health and economic burden.
Keywords: Absenteeism costs; Disability-adjusted life years; Healthcare costs; Musculoskeletal disorders.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

