Integrating pragmatic and implementation science randomized clinical trial approaches: a PRagmatic Explanatory Continuum Indicator Summary-2 (PRECIS-2) analysis
- PMID: 37085877
- PMCID: PMC10122352
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-023-07313-0
Integrating pragmatic and implementation science randomized clinical trial approaches: a PRagmatic Explanatory Continuum Indicator Summary-2 (PRECIS-2) analysis
Abstract
Background: Over the past two decades, pragmatic and implementation science clinical trial research methods have advanced substantially. Pragmatic and implementation studies have natural areas of overlap, particularly relating to the goal of using clinical trial data to leverage health care system policy changes. Few investigations have addressed pragmatic and implementation science randomized trial methods development while also considering policy impact.
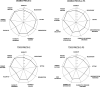
Methods: The investigation used the PRagmatic Explanatory Continuum Indicator Summary-2 (PRECIS-2) and PRECIS-2-Provider Strategies (PRECIS-2-PS) tools to evaluate the design of two multisite randomized clinical trials that targeted patient-level effectiveness outcomes, provider-level practice changes and health care system policy. Seven raters received PRECIS-2 training and applied the tools in the coding of the two trials. Descriptive statistics were produced for both trials, and PRECIS-2 wheel diagrams were constructed. Interrater agreement was assessed with the Intraclass Correlation (ICC) and Kappa statistics. The Rapid Assessment Procedure Informed Clinical Ethnography (RAPICE) qualitative approach was applied to understanding integrative themes derived from the PRECIS-2 ratings and an end-of-study policy summit.
Results: The ICCs for the composite ratings across the patient and provider-focused PRECIS-2 domains ranged from 0.77 to 0.87, and the Kappa values ranged from 0.25 to 0.37, reflecting overall fair-to-good interrater agreement for both trials. All four PRECIS-2 wheels were rated more pragmatic than explanatory, with composite mean and median scores ≥ 4. Across trials, the primary intent-to-treat analysis domain was consistently rated most pragmatic (mean = 5.0, SD = 0), while the follow-up/data collection domain was rated most explanatory (mean range = 3.14-3.43, SD range = 0.49-0.69). RAPICE field notes identified themes related to potential PRECIS-2 training improvements, as well as policy themes related to using trial data to inform US trauma care system practice change; the policy themes were not captured by the PRECIS-2 ratings.
Conclusions: The investigation documents that the PRECIS-2 and PRECIS-2-PS can be simultaneously used to feasibly and reliably characterize clinical trials with patient and provider-level targets. The integration of pragmatic and implementation science clinical trial research methods can be furthered by using common metrics such as the PRECIS-2 and PRECIS-2-PS. Future study could focus on clinical trial policy research methods development.
Trial registration: DO-SBIS ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00607620. registered on January 29, 2008. TSOS ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02655354, registered on July 27, 2015.
Keywords: Alcohol screening and brief intervention; Health care systems; Implementation science; PRECIS-2; PRECIS-2-PS; Policy; Posttraumatic stress disorder; Pragmatic clinical trials.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

