Electrolyte-Wettability Issues and Challenges of Electrode Materials in Electrochemical Energy Storage, Energy Conversion, and Beyond
- PMID: 37085907
- PMCID: PMC10265108
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202300283
Electrolyte-Wettability Issues and Challenges of Electrode Materials in Electrochemical Energy Storage, Energy Conversion, and Beyond
Abstract
The electrolyte-wettability of electrode materials in liquid electrolytes plays a crucial role in electrochemical energy storage, conversion systems, and beyond relied on interface electrochemical process. However, most electrode materials do not have satisfactory electrolyte-wettability for possibly electrochemical reaction. In the last 30 years, there are a lot of literature have directed at exploiting methods to improve electrolyte-wettability of electrodes, understanding basic electrolyte-wettability mechanisms of electrode materials, exploring the effect of electrolyte-wettability on its electrochemical energy storage, conversion, and beyond performance. This review systematically and comprehensively evaluates the effect of electrolyte-wettability on electrochemical energy storage performance of the electrode materials used in supercapacitors, metal ion batteries, and metal-based batteries, electrochemical energy conversion performance of the electrode materials used in fuel cells and electrochemical water splitting systems, as well as capacitive deionization performance of the electrode materials used in capacitive deionization systems. Finally, the challenges in approaches for improving electrolyte-wettability of electrode materials, characterization techniques of electrolyte-wettability, as well as electrolyte-wettability of electrode materials applied in special environment and other electrochemical systems with electrodes and liquid electrolytes, which gives future possible directions for constructing interesting electrolyte-wettability to meet the demand of high electrochemical performance, are also discussed.
Keywords: electrode materials; electrode/electrolyte interface; electrolyte-wettability; energy conversion; energy storage.
© 2023 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures













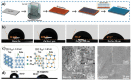


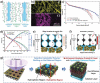

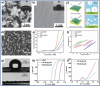

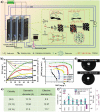
Similar articles
-
Electrolyte-philicity of electrode materials.Chem Commun (Camb). 2023 Jun 6;59(46):6969-6986. doi: 10.1039/d3cc00412k. Chem Commun (Camb). 2023. PMID: 37165689 Review.
-
Reliable Organic Carbonyl Electrode Materials Enabled by Electrolyte and Interfacial Chemistry Regulation.Acc Chem Res. 2024 Feb 6;57(3):375-385. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.3c00687. Epub 2024 Jan 19. Acc Chem Res. 2024. PMID: 38240205
-
Recent Advancements in Electrochemical Deposition of Metal-Based Electrode Materials for Electrochemical Supercapacitors.Chem Rec. 2022 Jul;22(7):e202200013. doi: 10.1002/tcr.202200013. Epub 2022 Mar 21. Chem Rec. 2022. PMID: 35313076 Review.
-
Opportunities of Flexible and Portable Electrochemical Devices for Energy Storage: Expanding the Spotlight onto Semi-solid/Solid Electrolytes.Chem Rev. 2022 Dec 14;122(23):17155-17239. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.2c00196. Epub 2022 Oct 14. Chem Rev. 2022. PMID: 36239919 Review.
-
Organic Electrode Materials for Energy Storage and Conversion: Mechanism, Characteristics, and Applications.Acc Chem Res. 2024 May 21;57(10):1550-1563. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.4c00016. Epub 2024 May 9. Acc Chem Res. 2024. PMID: 38723018
Cited by
-
A new thiol-sulfur click chemistry for lithium-organosulfide batteries.Innovation (Camb). 2025 Jan 13;6(2):100765. doi: 10.1016/j.xinn.2024.100765. eCollection 2025 Feb 3. Innovation (Camb). 2025. PMID: 39991483 Free PMC article.
-
High-capacity aqueous imidazolium-ion batteries enabled by MMZ-H+/H+ co-intercalation in a near neutral electrolyte.Chem Sci. 2025 Jun 3;16(27):12332-12342. doi: 10.1039/d5sc02677f. eCollection 2025 Jul 10. Chem Sci. 2025. PMID: 40510327 Free PMC article.
-
Transition metal phosphide/ molybdenum disulfide heterostructures towards advanced electrochemical energy storage: recent progress and challenges.RSC Adv. 2025 Apr 28;15(17):13397-13430. doi: 10.1039/d5ra01184a. eCollection 2025 Apr 22. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40297000 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Progress in Improving Rate Performance of Cellulose-Derived Carbon Materials for Sodium-Ion Batteries.Nanomicro Lett. 2024 Mar 11;16(1):148. doi: 10.1007/s40820-024-01351-2. Nanomicro Lett. 2024. PMID: 38466498 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From Small Data Modeling to Large Language Model Screening: A Dual-Strategy Framework for Materials Intelligent Design.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Dec;11(45):e2403548. doi: 10.1002/advs.202403548. Epub 2024 Oct 4. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 39364764 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mittal K. L., Contact Angle, Wettability and Adhesion, VSP/Brill, Leiden, Netherlands: 2009.
-
- Zhang X., Shi F., Niu J., Jiang Y., Wang Z., J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 621.
-
- Sun T., Feng L., Gao X., Jiang L., Acc. Chem. Res. 2005, 38, 644. - PubMed
-
- Liu K., Yao X., Jiang L., Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 3240. - PubMed
-
- Thomas P., Surf. Coat. Int. 1998, 81, 604.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
