Health related quality of life of patients following mechanical valve replacement surgery for rheumatic mitral stenosis in Tanzania
- PMID: 37085912
- PMCID: PMC10122295
- DOI: 10.1186/s13019-023-02235-z
Health related quality of life of patients following mechanical valve replacement surgery for rheumatic mitral stenosis in Tanzania
Abstract
Background: The assessment of outcomes of interventions based on the patient's perspective using patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs) has been increasingly highlighted in clinical practice. However, health related quality of life (HRQoL), one of the common constructs measured by PROMs remain unknown among patients after heart valve replacement (HVR) in Tanzania.
Objectives: To assess the HRQoL amongst patients operated on for rheumatic mitral stenosis at Jakaya Kikwete Cardiac Institute (JKCI).
Methods: A prospective study of patients operated on due to rheumatic mitral stenosis at JKCI from January 2020 to April 2021 was undertaken. The HRQoL was assessed by using the MacNew questionnaire, addressing three domains (physical, emotional, and social function); the score ranges from 0 to 7. We categorized HRQoL as low (mean score ≤ 4.9), moderate (5-6) and high (> 6). We analysed several sociodemographic and clinical variables for HRQoL.
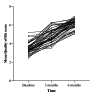
Results: Out of 54 patients, there were 34 females and 20 males. Their mean (± SD) age was 37.98 (± 12.58) years. The reliability of translated Kiswahili version of MacNew was good. The mean (± SD) global scores were 3.47 ± 0.59, 4.88 ± 0.71 and 6.14 ± 0.50 preoperatively, at 3 months and 6 months respectively (p-values < 0.001 preoperatively vs. 3 months, preoperatively vs. 6 months and at 3 months vs. 6 months). The median of individual mean difference HRQoL score pre-operatively and at 6 months was 2.67. The preoperative and 6 months mean difference HRQoL scores were higher among patients with vs. without atrial fibrillation (2.95 ± 0.59 vs. 2.45 ± 0.53, p = 0.003) and those on anticoagulants (preoperatively) vs. not on anticoagulants (3.14 ± 0.58 vs. 2.57 ± 0.57, 0.009). The mean difference HRQoL scores were similar for sociodemographic and other clinical parameters, including those with stroke vs. without stroke.
Conclusion: Six months after HVR the overall MacNew HRQoL scores improved markedly. This improvement in HRQoL was regardless of the presence of comorbidities (e.g. stroke and atrial fibrillation) which underscores the importance of considering valvular surgery if they fit the criteria. Clinicians and researchers in low-resource settings should collaborate to promote the utilization of PROMs in the routine care of patients.
Keywords: Health related quality of life; Interventions; Patient-reported outcome measures; Rheumatic heart disease.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests associated with this work.
Figures
References
-
- Mutagaywa RK, Chin A, Karaye K, Bonny A. Unmet needs in the management of arrhythmias among heart failure patients in Africa. Eur Heart J. 2022;00:1–3. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous