Fibroblast activation protein targeted radiotherapy induces an immunogenic tumor microenvironment and enhances the efficacy of PD-1 immune checkpoint inhibition
- PMID: 37086273
- PMCID: PMC10317891
- DOI: 10.1007/s00259-023-06211-6
Fibroblast activation protein targeted radiotherapy induces an immunogenic tumor microenvironment and enhances the efficacy of PD-1 immune checkpoint inhibition
Abstract
Purpose: FAP is a membrane-bound protease under investigation as a pan-cancer target, given its high levels in tumors but limited expression in normal tissues. FAP-2286 is a radiopharmaceutical in clinical development for solid tumors that consists of two functional elements: a FAP-targeting peptide and a chelator used to attach radioisotopes. Preclinically, we evaluated the immune modulation and anti-tumor efficacy of FAP-2287, a murine surrogate for FAP-2286, conjugated to the radionuclide lutetium-177 (177Lu) as a monotherapy and in combination with a PD-1 targeting antibody.
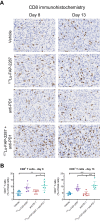
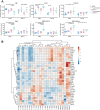
Methods: C57BL/6 mice bearing MCA205 mouse FAP-expressing tumors (MCA205-mFAP) were treated with 177Lu-FAP-2287, anti-PD-1, or both. Tumor uptake of 177Lu- FAP-2287 was assessed by SPECT/CT scanning, while therapeutic efficacy was measured by tumor volume and survival. Immune profiling of tumor infiltrates was evaluated through flow cytometry, RNA expression, and immunohistochemistry analyses.
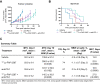
Results: 177Lu-FAP-2287 rapidly accumulated in MCA205-mFAP tumors leading to significant tumor growth inhibition (TGI) and longer survival time. Significant TGI was also observed from anti-PD-1 and the combination. In flow cytometry analysis of tumors, 177Lu-FAP-2287 increased CD8+ T cell infiltration which was maintained in the combination with anti-PD-1. The increase in CD8+ T cells was accompanied by an induction of STING-mediated type I interferon response and higher levels of co-stimulatory molecules such as CD86.
Conclusion: In a preclinical model, FAP-targeted radiotherapy enhanced anti-PD-1-mediated TGI by modulating the TME and increasing the recruitment of tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells. These findings provide a rationale for clinical studies of combined 177Lu-FAP-2286 radiotherapy and immune checkpoint inhibition in FAP-positive tumors.
Keywords: CD8; FAP; PD-1; STING; TRT; Theranostic.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
D. Zboralski, F. Osterkamp, A. Bredenbeck, A. Schumann, A. Hoehne, E. Schneider, M. Paschke, J. Ungewiss, C. Haase are employees of 3B Pharmaceuticals GmbH and are named inventors of FAP-2287. M. Paschke, and F. Osterkamp are cofounders of 3B Pharmaceuticals GmbH. E. Christensen is an employee of Minerva Imaging ApS. L. Robillard, A.D. Simmons, T.C. Harding and M. Nguyen are employees of Clovis Oncology, Inc., and may own stock or have stock options in the company.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

