A neuroprotective role of Ufmylation through Atg9 in the aging brain of Drosophila
- PMID: 37086384
- PMCID: PMC11073442
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-023-04778-9
A neuroprotective role of Ufmylation through Atg9 in the aging brain of Drosophila
Abstract
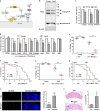
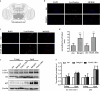
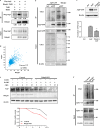
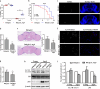
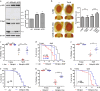
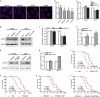
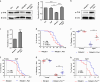
Ufmylation is a recently identified small ubiquitin-like modification, whose biological function and relevant cellular targets are poorly understood. Here we present evidence of a neuroprotective role for Ufmylation involving Autophagy-related gene 9 (Atg9) during Drosophila aging. The Ufm1 system ensures the health of aged neurons via Atg9 by coordinating autophagy and mTORC1, and maintaining mitochondrial homeostasis and JNK (c-Jun N-terminal kinase) activity. Neuron-specific expression of Atg9 suppresses the age-associated movement defect and lethality caused by loss of Ufmylation. Furthermore, Atg9 is identified as a conserved target of Ufm1 conjugation mediated by Ddrgk1, a critical regulator of Ufmylation. Mammalian Ddrgk1 was shown to be indispensable for the stability of endogenous Atg9A protein in mouse embryonic fibroblast (MEF) cells. Taken together, our findings might have important implications for neurodegenerative diseases in mammals.
Keywords: Life span; Oxidative stress; Patj; Puc; Uba5; Ufl1.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Switzerland AG.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
RCAD/Ufl1, a Ufm1 E3 ligase, is essential for hematopoietic stem cell function and murine hematopoiesis.Cell Death Differ. 2015 Dec;22(12):1922-34. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2015.51. Epub 2015 May 8. Cell Death Differ. 2015. PMID: 25952549 Free PMC article.
-
Atg9 antagonizes TOR signaling to regulate intestinal cell growth and epithelial homeostasis in Drosophila.Elife. 2017 Nov 16;6:e29338. doi: 10.7554/eLife.29338. Elife. 2017. PMID: 29144896 Free PMC article.
-
UFMylation of HRD1 regulates endoplasmic reticulum homeostasis.FASEB J. 2023 Nov;37(11):e23221. doi: 10.1096/fj.202300004RRRR. FASEB J. 2023. PMID: 37795761
-
UFL1, a UFMylation E3 ligase, plays a crucial role in multiple cellular stress responses.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Feb 10;14:1123124. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1123124. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36843575 Free PMC article. Review.
-
UFMylation: A Unique & Fashionable Modification for Life.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2016 Jun;14(3):140-146. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2016.04.001. Epub 2016 May 20. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 27212118 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multifaceted roles of UFMylation in health and disease.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025 Apr;46(4):805-815. doi: 10.1038/s41401-024-01456-9. Epub 2025 Jan 7. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025. PMID: 39775503 Review.
-
In vivo identification of Drosophila rhodopsin interaction partners by biotin proximity labeling.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 23;14(1):1986. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-52041-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38263196 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the role of ufmylation in the brain.Neural Regen Res. 2026 Feb 1;21(2):667-668. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-24-01311. Epub 2025 Jan 29. Neural Regen Res. 2026. PMID: 40326983 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Dapagliflozin Ameliorates Cognitive Impairment in Aluminum-Chloride-Induced Alzheimer's Disease via Modulation of AMPK/mTOR, Oxidative Stress and Glucose Metabolism.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 May 16;16(5):753. doi: 10.3390/ph16050753. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37242536 Free PMC article.
-
UFMylation: A Potential Modification for Neurological Diseases.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2025;23(8):907-917. doi: 10.2174/011570159X340639240905092813. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39757643 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Li H, Yu Z, Zhang W. Misfolded protein aggregation and altered cellular pathways in neurodegenerative diseases. STEMedicine. 2020;1(4):e63. doi: 10.37175/stemedicine.v1i4.63. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

