The global prevalence of myocardial infarction: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 37087452
- PMCID: PMC10122825
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-023-03231-w
The global prevalence of myocardial infarction: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Myocardial infarction (MI) is one of the life-threatening coronary-associated pathologies characterized by sudden cardiac death. The provision of complete insight into MI complications along with designing a preventive program against MI seems necessary.
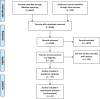
Methods: Various databases (PubMed, Web of Science, ScienceDirect, Scopus, Embase, and Google scholar search engine) were hired for comprehensive searching. The keywords of "Prevalence", "Outbreak", "Burden", "Myocardial Infarction", "Myocardial Infarct", and "Heart Attack" were hired with no time/language restrictions. Collected data were imported into the information management software (EndNote v.8x). Also, citations of all relevant articles were screened manually. The search was updated on 2022.9.13 prior to the publication.
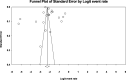
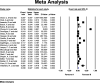
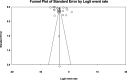
Results: Twenty-two eligible studies with a sample size of 2,982,6717 individuals (< 60 years) were included for data analysis. The global prevalence of MI in individuals < 60 years was found 3.8%. Also, following the assessment of 20 eligible investigations with a sample size of 5,071,185 individuals (> 60 years), this value was detected at 9.5%.
Conclusion: Due to the accelerated rate of MI prevalence in older ages, precise attention by patients regarding the complications of MI seems critical. Thus, determination of preventive planning along with the application of safe treatment methods is critical.
Keywords: Heart attack; MI; Myocardial infarction; Prevalence.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Hahla MS, Saeed Y, Razieh H. Comparison of risk factors & clinical and angiographic characterization of STEMI in young adults with older patients. Res J Pharm Biol Chem Sci. 2016;7(6):2013–2016.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

