Genetically engineered nanovesicles mobilize synergistic antitumor immunity by ADAR1 silence and PDL1 blockade
- PMID: 37087570
- PMCID: PMC10422002
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2023.04.011
Genetically engineered nanovesicles mobilize synergistic antitumor immunity by ADAR1 silence and PDL1 blockade
Abstract
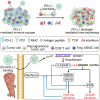
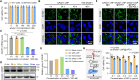
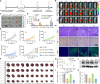
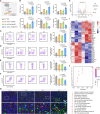
Growing evidence has proved that RNA editing enzyme ADAR1, responsible for detecting endogenous RNA species, was significantly associated with poor response or resistance to immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) therapy. Here, a genetically engineered nanovesicle (siAdar1-LNP@mPD1) was developed as an RNA interference nano-tool to overcome tumor resistance to ICB therapies. Small interfering RNA against ADAR1 (siAdar1) was packaged into a lipid nanoparticle (LNP), which was further coated with plasma membrane extracted from the genetically engineered cells overexpressing PD1. siAdar1-LNP@mPD1 could block the PD1/PDL1 immune inhibitory axis by presenting the PD1 protein on the coating membranes. Furthermore, siAdar1 could be effectively delivered into cancer cells by the designed nanovesicle to silence ADAR1 expression, resulting in an increased type I/II interferon (IFN-β/γ) production and making the cancer cells more sensitive to secreted effector cytokines such as IFN-γ with significant cell growth arrest. These integrated functions confer siAdar1-LNP@mPD1 with robust and comprehensive antitumor immunity, as evidenced by significant tumor growth regression, abscopal tumor prevention, and effective suppression of lung metastasis, through a global remodeling of the tumor immune microenvironment. Overall, we provided a promising translatable strategy to simultaneously silence ADAR1 and block PDL1 immune checkpoint to boost robust antitumor immunity.
Keywords: ADAR1 silence; PDL1 blocking; cancer immunotherapy; genetically engineered cell membrane; lipid nanoparticle.
Copyright © 2023 The American Society of Gene and Cell Therapy. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Loss of ADAR1 in macrophages in combination with interferon gamma suppresses tumor growth by remodeling the tumor microenvironment.J Immunother Cancer. 2023 Nov;11(11):e007402. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2023-007402. J Immunother Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37935565 Free PMC article.
-
Expanded human NK cells from lung cancer patients sensitize patients' PDL1-negative tumors to PD1-blockade therapy.J Immunother Cancer. 2021 Jan;9(1):e001933. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-001933. J Immunother Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33479024 Free PMC article.
-
Optimal Irreversible Electroporation Combined with Nano-Enabled Immunomodulatory to Boost Systemic Antitumor Immunity.Adv Healthc Mater. 2024 Mar;13(7):e2302549. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202302549. Epub 2023 Dec 13. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024. PMID: 38059737
-
The Era of Checkpoint Blockade in Lung Cancer: Taking the Brakes Off the Immune System.Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2017 Aug;14(8):1248-1260. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201702-152FR. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2017. PMID: 28613923 Review.
-
Resistance Mechanisms of Anti-PD1/PDL1 Therapy in Solid Tumors.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Jul 21;8:672. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00672. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32793604 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bioengineered therapeutic systems for improving antitumor immunity.Natl Sci Rev. 2024 Nov 12;12(1):nwae404. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwae404. eCollection 2025 Jan. Natl Sci Rev. 2024. PMID: 40114728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell Membrane-Camouflaged Nanoparticles Mediated Nucleic Acids Delivery.Int J Nanomedicine. 2023 Dec 28;18:8001-8021. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S433737. eCollection 2023. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023. PMID: 38164266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineered Cell Membrane-Camouflaged Nanomaterials for Biomedical Applications.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 Feb 23;14(5):413. doi: 10.3390/nano14050413. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38470744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer metastasis under the magnifying glass of epigenetics and epitranscriptomics.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2023 Dec;42(4):1071-1112. doi: 10.1007/s10555-023-10120-3. Epub 2023 Jun 28. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2023. PMID: 37369946 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological roles of A-to-I editing: implications in innate immunity, cell death, and cancer immunotherapy.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023 Jun 17;42(1):149. doi: 10.1186/s13046-023-02727-9. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37328893 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

