[M2 macrophage-derived exosomal lncRNA NR_028113.1 promotes macrophage polarization possibly by activating the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway]
- PMID: 37087583
- PMCID: PMC10122731
- DOI: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2023.03.08
[M2 macrophage-derived exosomal lncRNA NR_028113.1 promotes macrophage polarization possibly by activating the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway]
Abstract
Objective: To explore the effect of M2 macrophage-derived exosomal lncRNA NR_028113.1 on macrophage polarization and its possible mechanism.
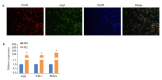
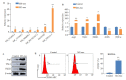
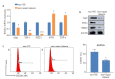
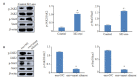
Methods: Bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) from BALB/c mice were isolated and cultured in vitro. After IL-4 treatment to induce M2 macrophage polarization, exosomes (M2-exo) were extracted from the supernatant of M2 macrophages and identified. The expression of lncRNA in M2-exo was detected by qRT-PCR. BMDMs were co-cultured with M2-exo (100 μg/mL) or PBS for 48 h, and the changes in cellular expression levels of Arg1, YM-1, FIZZ1, iNOS and TNF-α were detected using qRT-PCR and Western blotting. The percentage of CD206+ cells was analyzed using flow cytometry, and the phosphorylation levels of JAK2/STAT3 proteins were detected using Western blotting. A lncRNA smart silencer was designed to specifically inhibit the expression of lncRNA NR_028113.1 in the M2 macrophages, from which exosomes were extracted and co-cultured with BMDMs for 48 h. The mRNA expression levels of Arg1, YM-1, FIZZ1, iNOS and TNF-α, CD206+ cell percentage and the phosphorylation levels of JAK2/STAT3 proteins were detected using qRT-PCR, flow cytometry and Western blotting.
Results: LncRNA NR_028113.1 was highly expressed in the exosomes of M2 macrophages (P < 0.05). Co-culture with M2-exo significantly increased mRNA expressions of M2 macrophage marker genes Arg1, YM-1 and FIZZ1 (P < 0.05), lowered the expressions of iNOS and TNF-α (P < 0.05), and increased CD206+ cell percentage and JAK2/STAT3 protein phosphorylation level in BMDMs (P < 0.05). After inhibiting the expression of lncRNA NR_028113.1 in M2 macrophages, the extracted M2-exo caused significant down-regulation of the mRNA expressions of Arg1, YM-1 and FIZZ1 and up-regulation of iNOS and TNF-α mRNA (P < 0.05), resulting also in signi-ficantly reduced CD206+ cell percentage and lowered phosphorylation levels of JAK2/STAT3 proteins in co-cultured BMDM (P < 0.05).
Conclusions: M2 macrophage-derived exosomal lncRNA NR_028113.1 can significantly promote M2 polarization of macrophages possibly by activating the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway.
目的: 探究M2型巨噬细胞来源的外泌体lncRNA NR_028113.1对巨噬细胞极化的影响及机制。
方法: 体外分离并培养BALB/c小鼠骨髓来源的巨噬细胞(BMDMs),IL-4诱导其向M2型巨噬细胞极化后,提取并鉴定M2细胞上清液所分泌的外泌体exosome(M2-exo),qRT-PCR检测M2外泌体中lncRNA的表达。将100 μg/mL的M2-exo,对照组用等体积的PBS分别与M0巨噬细胞共孵育48 h后,qRT-PCR及Western blot检测各组细胞中Arg1、YM-1、FIZZ1、iNOS和TNF-α的表达,流式细胞术检测CD206+细胞比例,Western blot检测各组细胞JAK2/STAT3蛋白磷酸化水平。设计、合成lncRNA smart silencer特异性抑制lncRNA NR_028113.1的表达,转染M2细胞48 h后提取各组细胞(exo+NC和exo+smart silencer)上清液分泌的外泌体再与M0型巨噬细胞共孵育,检测孵育后各组细胞中Arg1、YM-1、FIZZ1、iNOS和TNF-α的表达以及CD206+细胞比例和JAK2/STAT3信号通路蛋白磷酸化水平。
结果: lncRNA NR_028113.1在M2型巨噬细胞外泌体中高表达(P < 0.05)。相比于PBS对照组,与M2-exo共培养的M0巨噬细胞中Arg1、YM-1和FIZZ1表达均显著上调(P < 0.05),iNOS和TNF-α表达显著下调(P < 0.05),CD206+细胞所占比例显著增加(P < 0.01),JAK2/STAT3蛋白磷酸化水平显著增加(P < 0.05)。抑制M2-exo中lncRNA NR_028113.1的表达后,共培养的M0巨噬细胞中Arg1、YM-1和FIZZ1表达显著下调(P < 0.05),iNOS和TNF-α表达显著上调(P < 0.05),CD206+细胞所占比例显著减少(P < 0.05),JAK2/STAT3蛋白磷酸化水平显著减少(P < 0.05)。
结论: M2型巨噬细胞来源的外泌体lncRNA NR_028113.1可显著促进巨噬细胞向M2型极化,其机制可能与激活JAK2/STAT3信号通路相关。
Keywords: JAK2; STAT3; exosomes; long non-coding RNA; macrophage polarization.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Exosomal AP000439.2 from clear cell renal cell carcinoma induces M2 macrophage polarization to promote tumor progression through activation of STAT3.Cell Commun Signal. 2022 Sep 24;20(1):152. doi: 10.1186/s12964-022-00957-6. Cell Commun Signal. 2022. PMID: 36153596 Free PMC article.
-
[Gastric cancer-derived mesenchymal stem cells regulate the M2 polarization of macrophages within gastric cancer microenvironment via JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2022 Jul 23;44(7):728-736. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112152-20200106-00008. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35880339 Chinese.
-
[miR-373 inhibits M2 polarization of tumor associated macrophages and affects rectal cancer cells by regulating JAK2/STAT6 signal pathway].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2025 Mar;41(3):211-220. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40145452 Chinese.
-
Long Non-coding RNAs Regulating Macrophage Polarization in Liver Cancer.Curr Pharm Des. 2024;30(27):2120-2128. doi: 10.2174/0113816128311861240523075218. Curr Pharm Des. 2024. PMID: 38859791 Review.
-
Exosomal Non-Coding RNA Mediates Macrophage Polarization: Roles in Cardiovascular Diseases.Biology (Basel). 2023 May 19;12(5):745. doi: 10.3390/biology12050745. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37237557 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Extracellular vesicles and macrophages in tumor microenvironment: Impact on cervical cancer.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 26;10(15):e35063. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35063. eCollection 2024 Aug 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39165926 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Overexpression of lncRNA HEM2M alleviates liver injury in mice with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2024 Jan 20;44(1):1-8. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.01.01. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2024. PMID: 38293970 Free PMC article. Chinese.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
