An algorithm for quantitatively estimating occupational endotoxin exposure in the biomarkers of exposure and effect in agriculture study: II. Application to the study population
- PMID: 37087683
- PMCID: PMC10265745
- DOI: 10.1002/ajim.23485
An algorithm for quantitatively estimating occupational endotoxin exposure in the biomarkers of exposure and effect in agriculture study: II. Application to the study population
Abstract
Background: We developed an algorithm to quantitatively estimate endotoxin exposure for farmers in the Biomarkers of Exposure and Effect in Agriculture (BEEA) Study.
Methods: The algorithm combined task intensity estimates derived from published data with questionnaire responses on activity duration to estimate task-specific cumulative endotoxin exposures for 13 tasks during four time windows, ranging from "past 12 months" to "yesterday/today." We applied the algorithm to 1681 participants in Iowa and North Carolina. We examined correlations in endotoxin metrics within- and between-task. We also compared these metrics to prior day full-shift inhalable endotoxin concentrations from 32 farmers.
Results: The highest median task-specific cumulative exposures were observed for swine confinement, poultry confinement, and grind feed. Inter-quartile ranges showed substantial between-subject variability for most tasks. Time window-specific metrics of the same task were moderately-highly correlated. Between-task correlation was variable, with moderately-high correlations observed for similar tasks (e.g., between animal-related tasks). Prior day endotoxin concentration increased with the total metric and with task metrics for swine confinement, clean other animal facilities, and clean grain bins.
Significance: This study provides insight into the variability and sources of endotoxin exposure among farmers in the BEEA study and summarizes exposure estimates for future investigations in this population.
Keywords: bioaersosol exposures; endotoxin exposures; farming activities; occupational questionnaires.
© 2023 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Figures
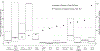

References
-
- Douwes J, Thorne P, Pearce N, et al. Bioaerosol health effects and exposure assessment: progress and prospects. Ann Occup Hyg 2003;47:187–200. - PubMed
-
- Thorne PS, Duchaine C, Blais Le Cours P. Airborne Bacteria, Archaea, and Endotoxin. In Yates M, Nakatsu C, Miller R, Pillai S, editors. Manual of Environmental Microbiology, 4th Edition. ASM Press; 2016.
-
- Basinas I, Elholm G, Wouters IM. Endotoxins, glucans and other microbial cell wall agents. In Viegas C, Viegas S, Gomes A, Täubel M, Sabino R, editors. Exposure to Microbiological Agents in Indoor and Occupational Environments Springer Berlin Heidelberg; 2017.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

