A novel CT image de-noising and fusion based deep learning network to screen for disease (COVID-19)
- PMID: 37088788
- PMCID: PMC10122759
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-33614-0
A novel CT image de-noising and fusion based deep learning network to screen for disease (COVID-19)
Abstract
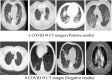
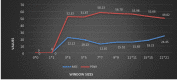
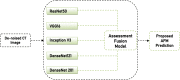
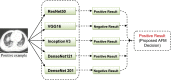
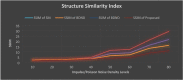
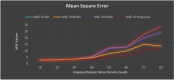
A COVID-19, caused by SARS-CoV-2, has been declared a global pandemic by WHO. It first appeared in China at the end of 2019 and quickly spread throughout the world. During the third layer, it became more critical. COVID-19 spread is extremely difficult to control, and a huge number of suspected cases must be screened for a cure as soon as possible. COVID-19 laboratory testing takes time and can result in significant false negatives. To combat COVID-19, reliable, accurate and fast methods are urgently needed. The commonly used Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction has a low sensitivity of approximately 60% to 70%, and sometimes even produces negative results. Computer Tomography (CT) has been observed to be a subtle approach to detecting COVID-19, and it may be the best screening method. The scanned image's quality, which is impacted by motion-induced Poisson or Impulse noise, is vital. In order to improve the quality of the acquired image for post segmentation, a novel Impulse and Poisson noise reduction method employing boundary division max/min intensities elimination along with an adaptive window size mechanism is proposed. In the second phase, a number of CNN techniques are explored for detecting COVID-19 from CT images and an Assessment Fusion Based model is proposed to predict the result. The AFM combines the results for cutting-edge CNN architectures and generates a final prediction based on choices. The empirical results demonstrate that our proposed method performs extensively and is extremely useful in actual diagnostic situations.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
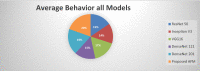
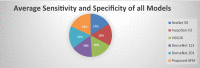
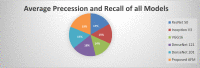
Similar articles
-
Deep Learning Algorithm for COVID-19 Classification Using Chest X-Ray Images.Comput Math Methods Med. 2021 Nov 9;2021:9269173. doi: 10.1155/2021/9269173. eCollection 2021. Comput Math Methods Med. 2021. PMID: 34795794 Free PMC article.
-
A deep learning algorithm using CT images to screen for Corona virus disease (COVID-19).Eur Radiol. 2021 Aug;31(8):6096-6104. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-07715-1. Epub 2021 Feb 24. Eur Radiol. 2021. PMID: 33629156 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis of COVID-19 using CT scan images and deep learning techniques.Emerg Radiol. 2021 Jun;28(3):497-505. doi: 10.1007/s10140-020-01886-y. Epub 2021 Feb 1. Emerg Radiol. 2021. PMID: 33523309 Free PMC article.
-
Thoracic imaging tests for the diagnosis of COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Sep 30;9:CD013639. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013639.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Nov 26;11:CD013639. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013639.pub3. PMID: 32997361 Updated.
-
Diagnostic performance of corona virus disease 2019 chest computer tomography image recognition based on deep learning: Systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Oct 21;101(42):e31346. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000031346. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36281129 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
COVID-19 infection segmentation using hybrid deep learning and image processing techniques.Sci Rep. 2023 Dec 20;13(1):22737. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-49337-1. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38123587 Free PMC article.
-
A hybrid optimization approach for accelerated multimodal medical image fusion.PLoS One. 2025 Jul 10;20(7):e0324973. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0324973. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40638635 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 infection analysis framework using novel boosted CNNs and radiological images.Sci Rep. 2023 Dec 9;13(1):21837. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-49218-7. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38071373 Free PMC article.
-
A Joint Classification Method for COVID-19 Lesions Based on Deep Learning and Radiomics.Tomography. 2024 Sep 5;10(9):1488-1500. doi: 10.3390/tomography10090109. Tomography. 2024. PMID: 39330755 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). Pneumonia of Unknown Cause–China. Emergencies Preparedness, Response, Disease Outbreak News. https://www.who.int/emergencies/disease-outbreak-news/item/2020-DON229 (2021).
-
- Siddiqui MK, Morales-Menendez R, Gupta PK, Iqbal HM, Hussain F, Khatoon K. Correlation between temperature and covid-19 (suspected, confirmed and death) cases based on machine learning analysis. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2020;14(suppl 1):1017–1024. doi: 10.22207/JPAM.14.SPL1.40. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

