Identification of Hub Genes and Immune Infiltration in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease -Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Bioinformatics Analysis
- PMID: 37089050
- PMCID: PMC10210691
- DOI: 10.5152/tjg.2023.22590
Identification of Hub Genes and Immune Infiltration in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease -Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Bioinformatics Analysis
Abstract
Background: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease has been a significant risk factor for hepatocellular carcinoma. In the study, we aimed to identify the key genes associated with the transition from non-alcoholic fatty liver disease to hepatocellular carcinoma through bioinformatics analysis.
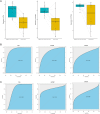
Methods: The GSE164760 dataset was used for identifying differentially expressed genes. Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes enrichment analysis were performed to explore the potential function of the differentially expressed genes. Subsequently, the protein-protein interaction network was constructed to select hub genes, and the immune cell infiltration was analyzed. Finally, the receiver operating characteristic analysis was performed to assess the diagnostic ability of the crucial genes.
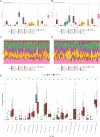
Results: A total of 156 differentially expressed genes were identified. Gene Ontology enrichment analysis indicated that differentially expressed genes were strongly associated with cellular hormone metabolic process, response to xenobiotic stimulus, collagen-containing extracellular matrix, detoxification, and regulation of growth. In the protein-protein interaction network, ESR1, CAT, CXCL8, CD4, SPP1, CYP2E1, CYP3A4, UGT2B7, GSTA1 and THBS1 were selected as the hub genes. Immune infiltration analysis demonstrated that M0 macrophages, plasma cells, CD8+T cell and M2 macrophages were significantly changed in tumor tissues. Finally, we verified the hub gene expression and selected CD4, UGT2B7, and CYP3A4 as the potential diagnostic biomarkers.
Conclusion: CD4, UGT2B7, and CYP3A4 were selected as the potential diagnostic biomarkers of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease-hepatocellular carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
