Towards continuous EIT monitoring for hemorrhagic stroke patients
- PMID: 37089433
- PMCID: PMC10115159
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1157371
Towards continuous EIT monitoring for hemorrhagic stroke patients
Abstract
The practical implementation of continuous monitoring of stroke patients by Electrical Impedance Tomography (EIT) is addressed. In a previous paper, we have demonstrated EIT sensitivity to cerebral hemodynamics, using scalp-mounted electrodes, very low-noise measurements, and a novel image reconstruction method. In the present paper, we investigate the potential to adapt that system for clinical application, by using 50% fewer electrodes and by incorporating into the measurement protocol an additional high-frequency measurement to provide an effective reference. Previously published image reconstruction methods for multi-frequency EIT are substantially improved by exploiting the forward calculations enabled by the detailed head model, particularly to make the referencing method more robust and to attempt to remove the effects of modelling error. Images are presented from simulation of a typical hemorrhagic stroke and its growth. These results are encouraging for exploration of the potential clinical benefit of the methodology in long-term monitoring of hemorrhagic stroke.
Keywords: electrical impedance tomography; image reconstruction; low-noise; multi-frequency; simulation; stroke.
Copyright © 2023 Ouypornkochagorn, Polydorides and McCann.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

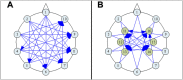
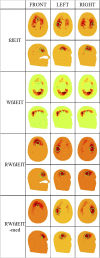
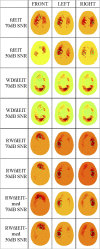


References
-
- Anas M., Norali A., Rehman M. (2012). Development of a low cost precision blood resistivity measurement device based on Thompson Lampard theorem. Penang, Malaysia: IEEE, 594–597.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

