How the use of an online healthcare community affects the doctor-patient relationship: An empirical study in China
- PMID: 37089478
- PMCID: PMC10117639
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1145749
How the use of an online healthcare community affects the doctor-patient relationship: An empirical study in China
Abstract
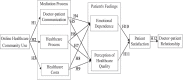
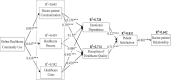
Possible improvements to the doctor-patient relationship are an important subject confronting national healthcare policy and health institutions. In recent years, online healthcare communities have changed the ways in which doctors and patients communicate, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic. However, previous research on how usage of online healthcare communities has affected the doctor-patient relationship is rather limited. This paper proposes a research model to investigate the relationship between online healthcare community usage and the doctor-patient relationship. An analysis of 313 patients' data using structural equation modeling showed the following. First, the use of an online healthcare community has a positive impact on doctor-patient communication, helps improve the performance of healthcare procedures, and reduces healthcare costs. Second, doctor-patient communication and healthcare costs have a positive impact on patients' emotional dependence and patients' perception of healthcare quality, while healthcare procedures do not have this impact. Finally, patients' emotional dependence and perception of healthcare quality have a positive effect on doctor-patient relationship through the mediator of patients' satisfaction.
Keywords: doctor–patient relationship; healthcare costs; online healthcare community; patients communicate; patients’ satisfaction.
Copyright © 2023 Wang, Zhang, Han, Zhao, Ma and Hao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antecedents and Consequences of Online Healthcare Community Usage: A Grounded Theory Approach.Healthcare (Basel). 2022 Sep 12;10(9):1749. doi: 10.3390/healthcare10091749. Healthcare (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36141361 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in Doctor-Patient Relationships in China during COVID-19: A Text Mining Analysis.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Oct 18;19(20):13446. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192013446. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36294022 Free PMC article.
-
General Perception of Doctor-Patient Relationship From Patients During the COVID-19 Pandemic in China: A Cross-Sectional Study.Front Public Health. 2021 Jul 6;9:646486. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.646486. eCollection 2021. Front Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34295863 Free PMC article.
-
The Voice of Chinese Health Consumers: A Text Mining Approach to Web-Based Physician Reviews.J Med Internet Res. 2016 May 10;18(5):e108. doi: 10.2196/jmir.4430. J Med Internet Res. 2016. PMID: 27165558 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of COVID-19 on the doctor-patient relationship in China.Front Public Health. 2022 Aug 1;10:907009. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.907009. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35979467 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Remote Patient Monitoring Using Mobile Health Technology in Cancer Care and Research: Patients' Views and Preferences.JCO Clin Cancer Inform. 2024 Nov;8:e2400092. doi: 10.1200/CCI.24.00092. Epub 2024 Nov 12. JCO Clin Cancer Inform. 2024. PMID: 39531613 Free PMC article.
-
Research on collaborative development mechanism of multiple stakeholders in medical institutions based on rough set.BMC Public Health. 2024 Feb 6;24(1):387. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-17813-6. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38321441 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of sense of security on job performance of medical staff: the mediating effect of psychological capital.Front Psychol. 2024 Apr 4;15:1347783. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1347783. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 38638512 Free PMC article.
-
Has China's hierarchical medical system improved doctor-patient relationships?Health Econ Rev. 2024 Jul 18;14(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s13561-024-00520-8. Health Econ Rev. 2024. PMID: 39023676 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and Evaluation of the Bidirectional Referral System in Internet Hospital: Case Study of Children's Hospital in Western China.J Med Internet Res. 2025 Jul 21;27:e69765. doi: 10.2196/69765. J Med Internet Res. 2025. PMID: 40690599 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang X, Ma L, Ma YB, Yang X. Mobile information systems usage and doctor-patient relationships: an empirical study in China. Mob Inf Syst. (2021) 2021:1–11. doi: 10.1155/2021/6684448 - DOI
-
- Liang CY, Gu DX, Tao FJ, Jain HK, Zhao Y, Ding B. Influence of mechanism of patient-accessible hospital information system implementation on doctor-patient relationships: a service fairness perspective. Inf Manag. (2017) 54:57–72. doi: 10.1016/j.im.2016.03.010, PMID: WOS:000392889100005 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical