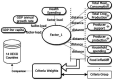
Food insecurity indicators of 14 OECD countries in a health economics aspect: A comparative analysis
- PMID: 37089487
- PMCID: PMC10117868
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1122331
Food insecurity indicators of 14 OECD countries in a health economics aspect: A comparative analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Food insecurity is a critical issue that refers to a lack of access to adequate food to support a healthy and active lifestyle. This problem has wide-reaching effects and can negatively impact health, education, and overall well-being. Addressing food insecurity requires a multifaceted approach that involves the efforts of governments, organizations, and individuals to ensure access to a balanced and nutritious diet for all.
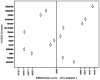
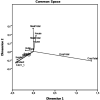
Methods: The aim of this study is to shed light on macro-level models and evaluate food insecurity risk in international comparisons. We considered six criteria to evaluate food insecurity risk in terms of health expenditure, gross domestic product (GDP) per capita, and GDP growth rate among 14 Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) countries. We developed a modeling approach in three stages to compare food insecurity risk and discussed the reasons for the rankings of the countries based on the model results.
Results: According to our findings, the United States has the lowest food insecurity risk, while Colombia has the highest. The results suggest that economic factors, such as GDP per capita and GDP growth rate, play a significant role in food insecurity risk. The study highlights the importance of addressing economic disparities and promoting economic growth to reduce food insecurity.
Discussion: This study provides insights into the relationship between food insecurity and economic factors, indicating that addressing economic disparities and promoting economic growth can reduce food insecurity. Future research using similar models to link economic outcomes with important health components such as nutrition and physical activity could provide a foundation for policy development.
Keywords: OECD countries; food insecurity; health economics; health policy; health spending.
Copyright © 2023 Yılmaz and Günal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
International health care spending.Health Aff (Millwood). 1986 Fall;5(3):111-22. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.5.3.111. Health Aff (Millwood). 1986. PMID: 3098657
-
The relationship between health expenditure indicators and economic growth in OECD countries: A Driscoll-Kraay approach.Front Public Health. 2022 Nov 21;10:1050550. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1050550. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36478719 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the relationships between health spending, treatable mortality and economic productivity in OECD countries.Front Public Health. 2022 Dec 21;10:1036058. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1036058. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36620274 Free PMC article.
-
[Literature review regarding the impact of population aging on healthcare expenditure growth: Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development member countries and Morocco].Pan Afr Med J. 2018 Oct 25;31:142. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2018.31.142.15248. eCollection 2018. Pan Afr Med J. 2018. PMID: 31037202 Free PMC article. Review. French.
-
Diet and Food and Nutrition Insecurity and Cardiometabolic Disease.Circ Res. 2023 Jun 9;132(12):1692-1706. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.123.322065. Epub 2023 Jun 8. Circ Res. 2023. PMID: 37289902 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Experiences of food insecurity in the Roma population before and during the COVID-19 lockdown in Spain.PLoS One. 2024 Jul 25;19(7):e0306471. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0306471. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39052644 Free PMC article.
-
Examining the interconnections among income, food prices, food insecurity, and health expenditure: a multicausality approach.BMC Public Health. 2025 Aug 14;25(1):2778. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-24153-6. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40813665
-
The Relationship Between Fast Food Consumption and Daily Lifestyle Changes During School Closures Following the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Cross-Sectional Study Among Adolescents in Korea.Psychiatry Investig. 2024 Jun;21(6):610-617. doi: 10.30773/pi.2023.0283. Epub 2024 Jun 24. Psychiatry Investig. 2024. PMID: 38960438 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding food loss patterns across developed and developing countries using a GDP, growth rate, and health expenditure-based typology.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 29;15(1):27597. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-13156-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40730623 Free PMC article.
-
Most vulnerable diet and health profiles: identifying countries at risk through a three-theme clustering.Front Public Health. 2025 Jul 7;13:1569755. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1569755. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40692892 Free PMC article.
References
-
- FAO . Declaration on World Food Security. World Food Summit. Rome: FAO; (1996).
-
- Misselhorn AA. What drives food insecurity in southern Africa? A meta-analysis of household economy studies. Glob Environ Chang. (2005) 15:33–43. doi: 10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2004.11.003 - DOI
-
- Khan SAR, Razzaq A, Yu Z, Shah A, Sharif A, Janjua L. Disruption in food supply chain and undernourishment challenges: an empirical study in the context of Asian countries. Socio Econ Plan Sci. (2022) 82:101033. doi: 10.1016/j.seps.2021.101033 - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources