Insulin amyloidosis: A case report
- PMID: 37089584
- PMCID: PMC10115977
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1064832
Insulin amyloidosis: A case report
Abstract
Insulin amyloidosis is a rare form of localized amyloidosis due to insulin aggregation into subcutaneous amyloid fibrils. We describe the case of a 55 years old male with insulin-requiring type 1 diabetes presenting with two non-inflammatory intra-dermal nodules associated with local lymph node enlargement. Diagnosis was confirmed by Congo red coloration of the amyloid deposit and insulin protein identification on mass spectrometry. Insulin amyloidosis is a potential complication of repeated subcutaneous insulin injections. The main risk factor is the intrinsic characteristic of the insulin used. Insulin amyloidosis leads to systemic metabolic consequences such as chronic hyperglycemia or unpredictable hypoglycemia, as well as unesthetic cutaneous lumps or abscesses. Standard-of-care is yet to be defined but mainly rely on therapeutical education of insulin injections, while surgical excision is reported to improve glycemic control in some patients.
Keywords: amyloidosis; case report; hyperglycemia; insulin; type 1 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest
Figures
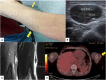
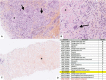
References
-
- Buxbaum JN, Dispenzieri A, Eisenberg DS, Fändrich M, Merlini G, Saraiva MJM, et al. . Amyloid nomenclature 2022: update, novel proteins, and recommendations by the International Society of Amyloidosis (ISA) nomenclature committee. Amyloid. (2022) 29:213–9. doi: 10.1080/13506129.2022.2147636, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Störkel S, Schneider HM, Müntefering H, Kashiwagi S. Iatrogenic, insulin-dependent, local amyloidosis. Lab Investig. (1983) 48:108–11. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

