Comprehensive genomic identification of cotton starch synthase genes reveals that GhSS9 regulates drought tolerance
- PMID: 37089638
- PMCID: PMC10113511
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1163041
Comprehensive genomic identification of cotton starch synthase genes reveals that GhSS9 regulates drought tolerance
Abstract
Introduction: Starch metabolism is involved in the stress response. Starch synthase (SS) is the key enzyme in plant starch synthesis, which plays an indispensable role in the conversion of pyrophosphoric acid to starch. However, the SS gene family in cotton has not been comprehensively identified and systematically analyzed.
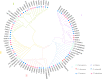
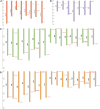
Result: In our study, a total of 76 SS genes were identified from four cotton genomes and divided into five subfamilies through phylogenetic analysis. Genetic structure analysis proved that SS genes from the same subfamily had similar genetic structure and conserved sequences. A cis-element analysis of the SS gene promoter showed that it mainly contains light response elements, plant hormone response elements, and abiotic stress elements, which indicated that the SS gene played key roles not only in starch synthesis but also in abiotic stress response. Furthermore, we also conducted a gene interaction network for SS proteins. Silencing GhSS9 expression decreased the resistance of cotton to drought stress. These findings suggested that SS genes could be related to drought stress in cotton, which provided theoretical support for further research on the regulation mechanism of SS genes on abiotic starch synthesis and sugar levels.
Keywords: GhSS9; VIGS; cotton; drought stress; gene network; starch synthase.
Copyright © 2023 Dai, Yang, Chen and Bai.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
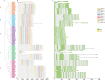


Similar articles
-
Comprehensive genomic characterization of cotton cationic amino acid transporter genes reveals that GhCAT10D regulates salt tolerance.BMC Plant Biol. 2022 Sep 15;22(1):441. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-03829-w. BMC Plant Biol. 2022. PMID: 36109698 Free PMC article.
-
Map-Based Functional Analysis of the GhNLP Genes Reveals Their Roles in Enhancing Tolerance to N-Deficiency in Cotton.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 8;20(19):4953. doi: 10.3390/ijms20194953. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31597268 Free PMC article.
-
Genome wide identification of GDSL gene family explores a novel GhirGDSL26 gene enhancing drought stress tolerance in cotton.BMC Plant Biol. 2023 Jan 7;23(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-04001-0. BMC Plant Biol. 2023. PMID: 36609252 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the Gh4CL gene family reveals a role of Gh4CL7 in drought tolerance.BMC Plant Biol. 2020 Mar 23;20(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-2329-2. BMC Plant Biol. 2020. PMID: 32293290 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide expression analysis of phospholipase A1 (PLA1) gene family suggests phospholipase A1-32 gene responding to abiotic stresses in cotton.Int J Biol Macromol. 2021 Dec 1;192:1058-1074. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.10.038. Epub 2021 Oct 14. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021. PMID: 34656543 Review.
References
-
- Berger S., Papadopoulos M., Schreiber U., Kaiser W., Roitsch T. (2010). Complex regulation of gene expression, photosynthesis and sugar levels by pathogen infection in tomato. Physiologia Plantarum 122, 419–428. doi: 10.1016/S0141-8130(98)00040-3 - DOI
-
- Brubaker C. L., Paterson A. H., Wendel J. F. (1999). Comparative genetic mapping of allotetraploid cotton and its diploid progenitors. Genome 42, 184–203. doi: 10.1139/gen-42-2-184 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

