Comparative analysis of seed and seedling irradiation with gamma rays and carbon ions for mutation induction in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 37089645
- PMCID: PMC10117944
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1149083
Comparative analysis of seed and seedling irradiation with gamma rays and carbon ions for mutation induction in Arabidopsis
Abstract
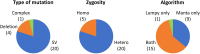
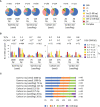
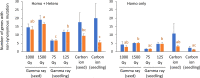
The molecular nature of mutations induced by ionizing radiation and chemical mutagens in plants is becoming clearer owing to the availability of high-throughput DNA sequencing technology. However, few studies have compared the induced mutations between different radiation qualities and between different irradiated materials with the same analysis method. To compare mutation induction between dry-seeds and seedlings irradiated with carbon ions and gamma rays in Arabidopsis, in this study we detected the mutations induced by seedling irradiation with gamma rays and analyzed the data together with data previously obtained for the other irradiation treatments. Mutation frequency at the equivalent dose for survival reduction was higher with gamma rays than with carbon ions, and was higher with dry-seed irradiation than with seedling irradiation. Carbon ions induced a higher frequency of deletions (2-99 bp) than gamma rays in the case of dry-seed irradiation, but this difference was less evident in the case of seedling irradiation. This result supported the inference that dry-seed irradiation under a lower water content more clearly reflects the difference in radiation quality. However, the ratio of rearrangements (inversions, translocations, and deletions larger than 100 bp), which are considered to be derived from the rejoining of two distantly located DNA breaks, was significantly higher with carbon ions than gamma rays irrespective of the irradiated material. This finding suggested that high-linear energy transfer radiation induced closely located DNA damage, irrespective of the water content of the material, that could lead to the generation of rearrangements. Taken together, the results provide an overall picture of radiation-induced mutation in Arabidopsis and will be useful for selection of a suitable radiation treatment for mutagenesis.
Keywords: Arabidopsis; carbon ion beam; gamma ray; mutation; structural variation.
Copyright © 2023 Hase, Satoh and Kitamura.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Physiological status of plant tissue affects the frequency and types of mutations induced by carbon-ion irradiation in Arabidopsis.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 23;8(1):1394. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-19278-1. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29362368 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison and Characterization of Phenotypic and Genomic Mutations Induced by a Carbon-Ion Beam and Gamma-ray Irradiation in Soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.).Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 16;24(10):8825. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108825. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37240171 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Consequences of Acute/Chronic Gamma and Carbon Ion Irradiation of Arabidopsis thaliana.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Mar 25;11:336. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00336. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 32273879 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Superiority of Heavy Charged-Particle Irradiation to X-Rays: Studies on Biological Effectiveness and Side Effect Mechanisms in Multicellular Tumor and Normal Tissue Models.Front Oncol. 2016 Feb 25;6:30. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2016.00030. eCollection 2016. Front Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26942125 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Production of specialized metabolites in plant cell and organo-cultures: the role of gamma radiation in eliciting secondary metabolism.Int J Radiat Biol. 2024;100(5):678-688. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2024.2324469. Epub 2024 Mar 7. Int J Radiat Biol. 2024. PMID: 38451191 Review.
Cited by
-
Mutagenesis of Highland barley (Hordeum vulgare L. Var. nudum) using nitrogen ion beam implantation: screening of phenotypic Var.ations and comparative transcriptome analysis.BMC Genomics. 2025 Jul 21;26(1):681. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11856-8. BMC Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40691530 Free PMC article.
-
A self-compatible pear mutant derived from γ-irradiated pollen carries an 11-Mb duplication in chromosome 17.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Mar 5;15:1360185. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1360185. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38504898 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing the structural variations in the genome of the mandarin variety, IrM2, induced by gamma irradiation.Plant Biotechnol J. 2025 Sep;23(9):3814-3823. doi: 10.1111/pbi.70205. Epub 2025 Jun 15. Plant Biotechnol J. 2025. PMID: 40517402 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and Characterization of High-Temperature-Tolerant Mutants of Bradyrhizobium diazoefficiens USDA110 by Carbon-Ion Beam Irradiation.Microorganisms. 2024 Sep 2;12(9):1819. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12091819. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39338493 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Calugaru V., Nauraye C., Noël G., Glocanti N., Favaudon V., Mégnin-Chanet F. (2011). Radiological characterization of two therapeutic proton beams with different initial energy spectra used at the institut curie proton therapy center in orsay. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 81, 1136–1143. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.09.003 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

