Diagnostic Utility of Nailfold Capillaroscopy using Hand-held Dermoscope in Systemic Sclerosis
- PMID: 37089847
- PMCID: PMC10115326
- DOI: 10.4103/idoj.idoj_361_22
Diagnostic Utility of Nailfold Capillaroscopy using Hand-held Dermoscope in Systemic Sclerosis
Abstract
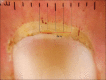
Introduction: The pathogenesis in systemic sclerosis (SSc) mainly involves vascular injury, fibrosis, and immune activation. Visualization of these microvascular changes by nailfold capillaroscopy (NFC) can help in the early diagnosis of the disease. Even though the gold standard for NFC is a videodermoscope, the ease, practicality, and accessibility make the hand-held dermoscope a more versatile and suitable device in the hands of the dermatologists in the busy outpatient department.
Aim: To study the pattern of nail fold capillaries using hand-held dermoscope in the patients of SSc and correlate the findings with disease severity.
Materials and methods: An observational, cross-sectional hospital-based study was carried out over a span of 2 years, from January 2020 till December 2021, in 50 patients of SSc. NFC using DermLite DL4 was performed in all the patients and distribution, morphology, density of capillaries, and nail fold capillary pattern were observed.
Results: Out of 50 patients, 38 patients had diffuse type of disease, and 12 had limited type of disease. The mean capillary density in our patients was 4.7 ± 0.81/mm. Dilated capillaries was the most common NFC finding (80%), whereas active scleroderma pattern was the most common pattern (56%). A significant association was found between the type of capillary pattern and duration of disease, type of disease, and cutaneous manifestations.
Conclusion: Hand-held dermoscope is reliable, practical, and assessable tool that aids in early diagnosis of the disease and also helps in assessing the severity and prognosis of SSc.
Keywords: Hand-held dermoscope; nailfold capillaroscopy; systemic sclerosis.
Copyright: © 2023 Indian Dermatology Online Journal.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Nailfold digital capillaroscopic findings in patients with diffuse and limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis.Reumatologia. 2017;55(1):15-23. doi: 10.5114/reum.2017.66683. Epub 2017 Mar 22. Reumatologia. 2017. PMID: 28386138 Free PMC article.
-
Methods of Assessing Nailfold Capillaroscopy Compared to Video Capillaroscopy in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis-A Critical Review of the Literature.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jun 28;13(13):2204. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13132204. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37443598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nailfold capillaroscopy by digital microscope in an Indian population with systemic sclerosis.Int J Rheum Dis. 2012 Feb;15(1):95-101. doi: 10.1111/j.1756-185X.2011.01699.x. Epub 2011 Dec 4. Int J Rheum Dis. 2012. PMID: 22324952
-
Nailfold capillaroscopy and autoimmune connective tissue diseases in patients from a Portuguese nailfold capillaroscopy clinic.Rheumatol Int. 2020 Feb;40(2):295-301. doi: 10.1007/s00296-019-04427-0. Epub 2019 Aug 26. Rheumatol Int. 2020. PMID: 31451935
-
Nailfold capillaroscopy in systemic diseases: short overview for internal medicine.Rom J Intern Med. 2021 Aug 26;59(3):201-217. doi: 10.2478/rjim-2021-0007. Print 2021 Sep 1. Rom J Intern Med. 2021. PMID: 33600677 Review.
References
-
- Perelas A, Arrossi AV, Highland KB. Pulmonary manifestations of systemic sclerosis and mixed connective tissue disease. Clin Chest Med. 2019;40:501–18. - PubMed
-
- Cutolo M, Sulli A, Secchi ME, Paolino S, Pizzorni C. Nailfold capillaroscopy is useful for the diagnosis and follow-up of autoimmune rheumatic diseases. A future tool for the analysis of microvascular heart involvement? Rheumatology (Oxford) 2006;45:iv43–6. - PubMed
-
- Cutolo M, Sulli A, Pizzorni C, Accardo S. Nailfold videocapillaro-scopy assessment of microvascular damage in systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol. 2000;27:155–60. - PubMed
-
- Ankad BS, Jaju PS. Nailfold capillaries in connective tissue diseases in skin of color:A dermoscopic view. Clin Dermatol Rev. 2019;3:115–20.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

