Neglected intrapulmonary arteriovenous anastomoses: A comparative study of pulmonary right-to-left shunts in patients with patent foramen ovale
- PMID: 37089892
- PMCID: PMC10117845
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1111818
Neglected intrapulmonary arteriovenous anastomoses: A comparative study of pulmonary right-to-left shunts in patients with patent foramen ovale
Abstract
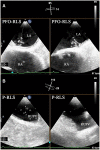
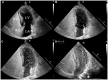
Objective: Pulmonary right-to-left shunt (P-RLS) and patent foramen ovale right-to-left shunt (PFO-RLS) often appear in combination, and there are often differences and connections between them. Intrapulmonary arteriovenous anastomoses (IPAVAs), as part of P-RLS, are often overlooked because there are no technologies to detect and identify them. This study aimed to further clarify the incidence and characteristics of P-RLS with the help of contrast transesophageal echocardiography (c-TEE) and contrast transthoracic echocardiography (c-TTE), providing a reference for clinically relevant research and patent foramen ovale (PFO) management disposal decisions.
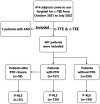
Methods: We retrospectively investigated 414 subjects who came to our hospital for c-TEE from October 2021 to July 2022, and all subjects completed c-TTE simultaneously. 7 Patients who were newly diagnosed with an atrial septal defect were excluded. Eventually, 407 patients were included in this study. Among them, 157 patients with PFO (58 patients were treated with PFO closure subsequently) and 250 patients without PFO confirmed by c-TEE were finally enrolled. In the process, we observed and analysed the presence of P-RLS.
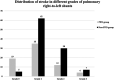
Results: A total of 407 patients were included in the final analysis and divided into PFO group (N = 157) and non-PFO group (N = 250) according to the results of c-TEE. Whether at rest or after Valsalva maneuver, the incidence of P-RLS was significantly higher under c-TEE than under c-TTE in the two groups (P < 0.001). For both c-TTE and c-TEE, the incidence of P-RLS was slightly higher after Valsalva maneuver than at rest, but the difference was not significant (c-TTE: rest vs. Valsalva maneuver, P = 0.214; c-TEE: rest vs. Valsalva maneuver, P = 0.076). The Valsalva maneuver increased the incidence of P-RLS in the group without PFO, which was more significant in c-TEE (c-TTE: rest vs. Valsalva maneuver, P = 0.591; c-TEE: rest vs. Valsalva maneuver, P = 0.008). In both groups, the P-RLS semiquantitative grading was statistical significance under different states and examinations (P < 0.001).
Conclusion: The vast majority of P-RLS are grade 1-2 and are derived from physiological IPAVAs. Even so, attention should be given to the differentiation between P-RLS and PFO-RLS. c-TEE is an effective method to detect P-RLS; however, the recruitments of c-TEE and Valsalva maneuver to P-RLS should be noted.
Keywords: intrapulmonary arteriovenous anastomoses; patent foramen ovale; pulmonary right-to-left shunt; saline contrast echocardiography; transesophageal echocardiography; transthoracic echocardiography.
© 2023 Chen, Zhu, Zhu, Tang, Li, Zhang, Zhao, Ma and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Importance of adequately performed Valsalva maneuver to detect patent foramen ovale during transesophageal echocardiography.J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2013 Nov;26(11):1337-43. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2013.07.016. Epub 2013 Aug 28. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2013. PMID: 23993693
-
Contrast-enhanced transthoracic echocardiography applied in evaluation of pulmonary right-to-left shunt: A preliminary study.Comput Med Imaging Graph. 2018 Sep;68:55-60. doi: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2018.04.007. Epub 2018 Apr 27. Comput Med Imaging Graph. 2018. PMID: 30056290
-
Assessment of the Characteristics of Patent Foramen Ovale Associated with Cryptogenic Stroke.Curr Med Imaging. 2024;20:e15734056284889. doi: 10.2174/0115734056284889240102095034. Curr Med Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38415485
-
Accuracy of conventional transthoracic echocardiography for the diagnosis of intracardiac right-to-left shunt: a meta-analysis of prospective studies.Echocardiography. 2014 Oct;31(9):1036-48. doi: 10.1111/echo.12583. Epub 2014 Apr 2. Echocardiography. 2014. PMID: 24689727
-
The diagnostic value of contrast-enhanced transcranial Doppler and contrast-enhanced transthoracic echocardiography for right to left shunt in patent foramen ovale: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Neurol. 2024 Aug 2;15:1447964. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1447964. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39157064 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of intrapulmonary arteriovenous anastomoses before and after oxygen supplementation, using transthoracic agitated saline contrast echocardiography in rescued Korean raccoon dogs.Front Vet Sci. 2024 Aug 8;11:1362363. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1362363. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 39176393 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic variation in patent foramen ovale: a case-control genome-wide association study.Front Genet. 2025 Jan 13;15:1523304. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1523304. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2025. PMID: 39872005 Free PMC article.
-
The clinical diagnostic value of right-to-left shunt in cryptogenic stroke under right heart contrast echocardiography: a retrospective case-control study.Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2024 Dec 31;14(6):1048-1057. doi: 10.21037/cdt-24-288. Epub 2024 Dec 19. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2024. PMID: 39790191 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the Application Value of Transthoracic Echocardiography in Diagnosing Patent Foramen Ovale Under Different States of Stimulation: A Retrospective Study.Clin Cardiol. 2024 Aug;47(8):e24319. doi: 10.1002/clc.24319. Clin Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 39109504 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

